An article recently published in the Indian express recently and here is the concise summary of the article:
India’s policy of strategic autonomy has been its hallmark, and it has enjoyed since the Cold war era. But what is it, and how does this apply to India’s roles in both the Quad and BRICS? Let’s break it down:
Strategic Autonomy Defined
In the early 1990s, the very idea of strategic autonomy is in large part about carving out a place for India in the face of a dominant America. During that time the conflict involved India concerned the Kashmir issue as well as India’s nuclear plans.Mr. Clinton’s questioning of accession of Jammu and Kashmir to India and the subsequent intention of the United States to cap India’s nuclear and missile development has led to this assertiveness.
Transformation of India-U.S. Relations
India and the United States have been great powers with dynamic bilateral relations over the last three decades. Here are some key elements:
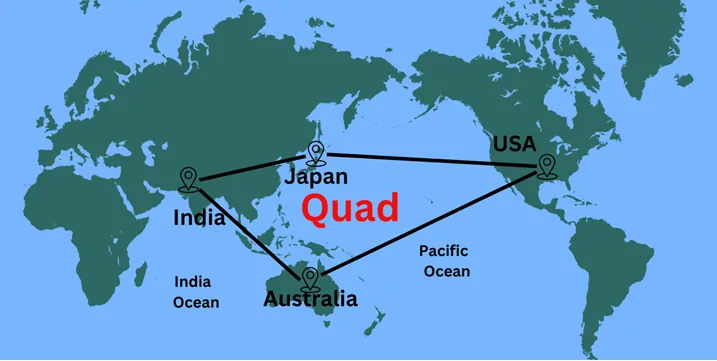
- China Challenge: When China’s aggression began rising, America became important for India. The grouping of four countries which is called Quad is India, the United States of America, Japan, and Australia which have emerged due to the China’s growth.
- Kashmir and Cross-Border Terrorism: India, supported by the US and other nations on the Kashmir issue, a force on Pakistan in cross border terror.
- Nuclear Order and UNSC Membership: The U.S. supported India’s entry into the nuclear supplier group and nuclear deal and supports Indian UNSC membership.
- Trade Diversification: The Quad partners are interested in diversifying their economies to free themselves from the dominance of China, which is the goal of India.
- Opposition to BRI: India does not support China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) because the infrastructure plan challenges territorial sovereignty and regional dominance. It is for the mentioned reason that the Quad partners convene their cooperation efforts in the area of new-generation infrastructure.
The Quad vs. BRICS: The Global Times, a Chinese newspaper, recently highlighted what it sees as a contradiction: The engagement of India in both Quad and BRICS.The paper is devoted to the idea that the Indian orientation to the USA hinders Indian relations with China and Russia and development of BRICS and SCO.
The Quad

Origins and Purpose
The Quad came to existence around mid-2000s but actively revived in recent time. Such a concept is not a conventional security alliance and is therefore better viewed as a concept of a particular vision than as an organized and well-defined military cooperation.The main aspect of its focus is to enhance a liberal, outward-looking Indo-Pacific configuration. In doing so, it is aspiring to become a powerful counterweight to China, as well as a defender of the liberal paradigm of international relations.
Member Nations
- Australia: In the context of the Indo-Pacific, Australia offers maritime capabilities, economic power, and willingness to maintain the region secure.
- India: India’s is adding a large piece of territory to its strategic map, strengthen maritime security and support democratic principles.
- Japan: Japan brings technology, money, workforce and firm support for international organizations.
- United States: The U.S contributes military force, financial muscle and strategic direction. This is true since its participation in the Quad demonstrates its interest in the region.
Objectives
- Security and Stability: The Quad seeks to provide for the secure and stable Indo-Pacific region. This includes dealing with challenges like piracy, terrorism and other form of unlawful acts including acts of illicit trafficking.
- Economic Prosperity: The most important characteristic of the relations is economic collaboration. The Quad aims to build relations, infrastructure and trade, for economic development for all the associated members.
- Resilience and Preparedness: Duties include disaster response and emergency management, disaster prevention and humanitarian aid, and members’ climate preparedness.
- Technology and Cyber security: Responding to new threats, such as modern and important technologies, cyber threats, and fake, false information.
Strategy for the Indo-Pacific
- Maritime Security: Quad works as a maritime security diamond which includes safety in sea routes, shared patrols and intelligence. It is intended to prevent provocation and to act immediately when something like this occurs.
- Investing in ASEAN: The Quad appreciates the role of Southeast Asia and approaches the ASEAN nations. It aims at establishing and enhancing collaborations as well as enhancing regional security.
- Balancing China: Though not antagonistic to China, the Quad offers an Asia that China is not writing, an Asia of rules based international order. This increases the compliance with responsible behaviour and international standards.
All in all, the Quad is not simply a diplomatic geometry; it represents the intent to collectively chart the course for the Indo-Pacific. While the region is grappling with an increasingly complicated set of challenges, this strategic vision possibilities-oriented, community-engaging, and prospective is truly transformative.
Quad and India
Counterbalancing China
The Quad is especially important for India as it offers it a necessary tool to effectively respond to China’s aggressive behaviour on the territory of the Indo-Pacific region. India has recently been having border issues with China up to early last year, and having friends that have similar issues makes a lot of sense.Notably, the Quad is a coalition offour large democracies but does not configure or designate any nation as an adversary while its formation inherently puts check on China’s aggressive diplomacy.
Diplomatic Space and Strategic Autonomy
While the Quad is not militarybased alliance, it offers India an opportunity to interact with the US as well its Asian counterparts without formal commitments. This also fits with India’s proclaimed strategic culture of strategic freedom.India can still join regional cooperation, swap information, and coordinate on numerous fronts without committing to predictable roles.
Unity in the Indo-Pacific
The Quad shows that nations are jointly combating various adversities. Something like a superhero team is ready to combat a supervillain which is synonymous with China’s assertiveness in the scenario.On problems such as territorial integrity, sovereignty or addressing and settling disputes peacefully, Quad promotes the notion that the rules-based international order is important.
Beyond Security: A Holistic Approach
The Quad’s recent initiatives span diverse areas: healthcare, infrastructure development, emerging technologies and other. It’s not about hegemony; it is about constructing the future of the Indo-Pacific region that is strong and prosperous.To the Indian people, it implies a chance to develop using the best world technology, bilateral cooperation in terms of disaster preparedness, and trade relations.
ASEAN Acceptance
The Quad has gone through its best to ensure that it does not be seen as the “Asian NATO.” It interacts with the ASEAN countries and proposes itself to them.ASEAN states find it reasonable the Quad is not a military alliance club; it is a cooperation platform.
Conclusion
The Quad cannot be viewed only as a military exercise; it has become one of the main platforms for testing India’s independent foreign policy. It enables India to get involved, cooperate and manoeuvre through the multifaceted Indo-Pacific environment without committing India to any particular affiliation.
Challenges associated with Quad
Diverse Priorities and Perspectives
- Challenge: Every Quad member has its own agenda of priorities, threats, and interests in the geography it operates in. As for example, owing to differences on border issues and power structures, India has a different perception about China.
- Solution: That these differences exist does not mean that the cooperative effort must suffer or cannot work. There are many issues that India, Japan, Australia, and the United States share with regard to security interests such as balance of power, freedom of navigation in the South China Sea, and resistance to BRI and debt-trap diplomacy. Where there are differences, key priorities can be a powerful motivator to focus on what it is that everyone wants to achieve.
China’s Reaction and Deterrence
- Challenge: China pays much attention to the activities of Quad. Any such step seen as containing could elicit a reaction and may eventually heighten tensions.
- Solution: It should be therefore clear what has been announced as Quad’s purpose: not as an anti-China organization but an organization that wants to uphold the rules-based order. More military cooperation exercises, information exchange and compatibility have a possibility to strengthen the deterrence without creating dilettante confrontation.
Economic Dependence on China
- Challenge: Members of Quad have an economic relation with China. Economic interests apart from security are easily influenced and are hard to balance on most agendas.
- Solution: Encountering the BRI (Belt and Road Initiative) and founding an alternative. An Indo-Pacific critical infrastructure funding scheme would provide small states with an opportunity to finance their projects other than the BRI projects that makes them heavily dependent on China.
Domestic Politics and Commitment Levels
- Challenge: Ideally, each member has domestic pressures, providing or competing for different priorities. For Quad cooperation to continue there needs to be firm commitment.
- Solution: This could be through the high level diplomacy dialogues, joint statements, speeches, and practical undertakings. The Quad should have crunch initiatives and those outcomes that are more tangible such as in the technology sector, disaster management, or climate change in order to keep the business moving forward.
Avoiding Militarization Perceptions
- Challenge: Many people are concerned that the Quad may gradually transform into a military bloc, which will endanger the stability in the region.
- Solution: Cooperation in the military domain is still necessary, but the focus on the Quad’s comprehensive anymore of cooperation ranging from economic security to health and climate change is productive. Such apprehension can be calmed by honest communication about purpose.
ASEAN Centrality and Regional Sensitivities
- Challenge: The consequence of the aforementioned great power competition was that South East Asian countries become concerned with entrapment. ASIAN is an important organisation that can’t be ignored.
- Solution: In relation to its position as a group of four, the Quad should take an interest in ASEAN, include it in its conversations, and promote regional processes. This analysis will show that the Quad does not threaten ASEAN but instead can promote cooperation because Quad activities are synergistic with ASEAN arrangements.
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD) is the kind where it is changing into a trade organization from a military coalition, in the present context. Is it so?
The QUAD has changed beyond recognition in the recent years. At its inception, the QUAD was seen mainly with the emphasis on military shared security concerns of countries of the Indo-Pacific region but there has been a broadening of agenda in recent years. Today, it is on the edge of global and regional politics, economy and cooperation.
The Military Alliance Phase
In its first three decades of existence, the QUAD’s central focus was military collaboration. This led to daily boat operations, manoeuvring, and regular, joint patrol and information exchange. The member countries intended to improve compatibility and act in unison regarding the threats to the area’s security. China saw the QUAD as a foil, which is aimed at constraining its growth.
The Trade Bloc Transformation
Time has changed and so did the QUAD, The QUAD of the past, however, look strikingly different today. But at the same time economic cooperation has become as important as security issues are still worrying. Here’s how the transformation unfolded:
- Supply Chain Resilience: COVID-19 was a wake-up call to many countries and global leaders in respect to their respective supply chain systems. The QUAD nations recognized the need to diversify production and reduce dependence on a single country (like: China) and how to build a supply chain that cannot be disrupted during such emergencies.
- Infrastructure Investment: The QUAD started to extend its agenda from military infrastructure to economic infrastructure. One example of this trend is the “Blue Dot Network” an effort meant to identify high-quality infrastructure investments. Connectivity, energy, and digital infrastructure are essential, correlating QUAD’s vision, striving to promote economic development and security.
- Trade and Investment: There’s been an improvement in the trade relation among QUAD member countries. The latest developments have been observed in the logic of bilateral trade liberalization, investment promotion, and high technology cooperation. The QUAD is therefore pitching itself as an option to the China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Climate Change and Green Tech: The QUAD has been brought closer by environmental challenges. The cooperation on clean energy, climate resilience, and sustainable development is steadily increasing.
Challenges Ahead
Despite its evolution, the QUAD faces several hurdles:
- China’s Reaction: QUAD has been closely observed by Beijing. It means that any attempt to find containment in such a system could worsen the situation.
- Divergent Interests: The four members of the equation have focuses of varying kinds. Security, economic and interests as well as balance of power in the region is a very delicate act that needs diplomacy.
- Inclusivity: The QUAD therefore needs to draw in other regional actors including ASEAN for it not to be perceived as a group that is exclusionary.