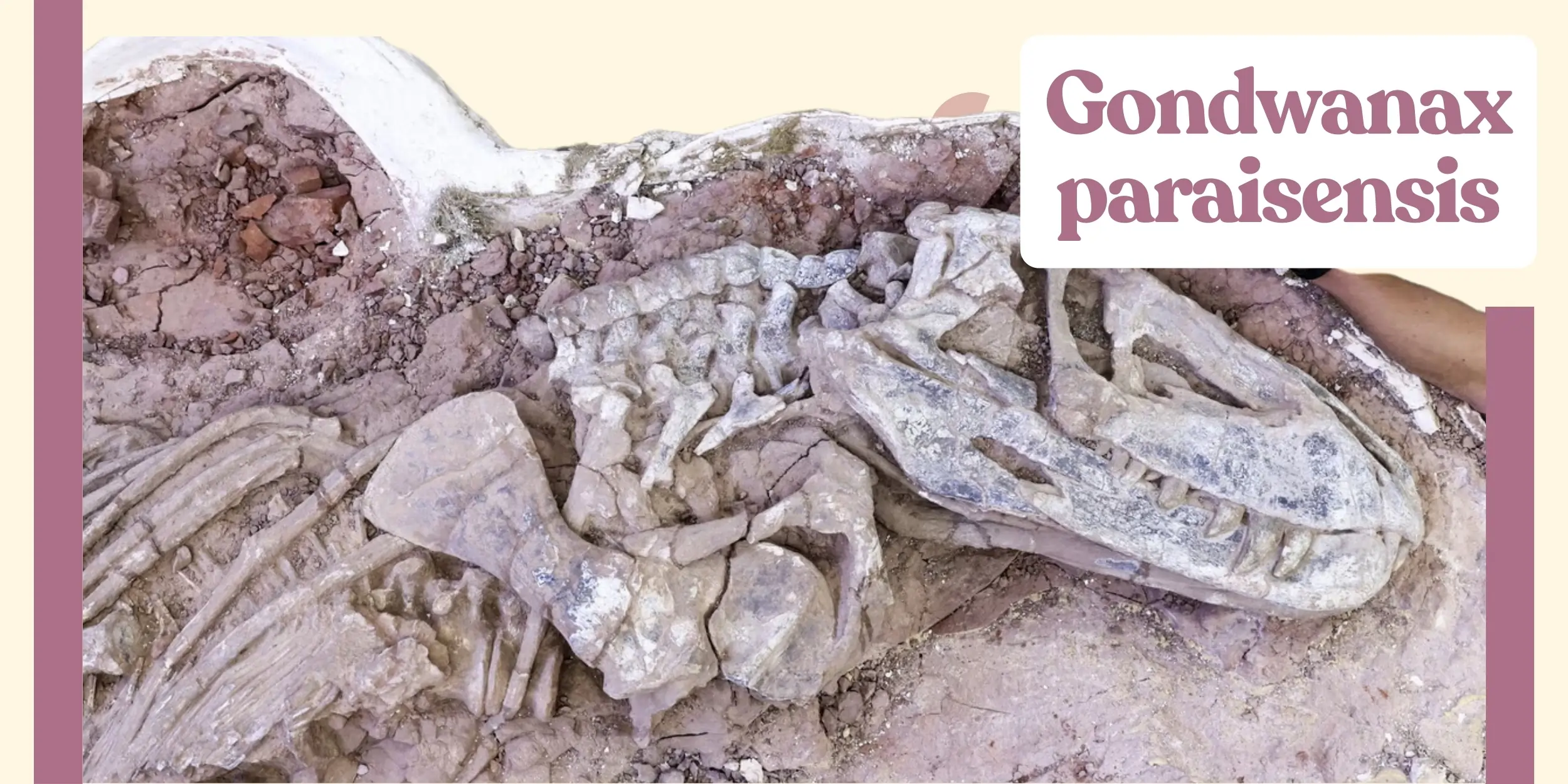
The Gondwanax paraisensis discovery has made new opportunity to understanding dinosaurs’ evolution. This small four legged reptile that is about the size of a dog lived for about 237 million years in the Triassic era. The subject of this description is an herbivore dinosaur species, Gondwanax paraisensis, was discovered in the town of Paraiso do Sul in southern Brazil.
Discovery and Naming
Gondwanax paraisensis, a fossil was first found in February of 2014 by Pedro Lucas Porcela Aurelio who is a physician but palaeontology enthusiast. Aurelio discovered the fossil in one of the sequences in the Pinheiros-Chiniquá Sequence of the Santa Maria Supersequence in Rio Grande do Sul. For this reason, he presented the fossil to a local university in 2021 to undertake various analyses.
The part of the genus name comes from the name of the old South American formation Gondwana, the second part is the Greek word “anax,” meaning “lord” or “king” reflecting the dominance of dinosauromorphs in the Mesozoic Era. This species name paraisensis is related to the location of discovery, the Municipality of Paraiso do Sul.
Physical Characteristics
One meter in length and with an estimated mass of 3 to 6 kilograms. That is why many of its features, such as its light body and long tail, indicate that the animal could be hunters’ perfect travel companion. It is associated with the preserved elements a right femur, cervical and dorsal vertebrae, sacral vertebrae and an incomplete pelvic girdle. For instance, Gondwanax paraisensis possesses a sacral condition of three vertebrae in the sacrum, although it only has a total of 19 presacral vertebrae; such a condition is considered to be an attribute of more evolved dinosaurs.
Importance
Gondwanax paraisensis is, in fact, one of the oldest identified members of the Silesauridae, which are a group of reptiles, related to actual dinosaurs. Maturity is observed in the representation of such a characteristic feature as three sacral vertebrae – this indicates that Gondwanax paraisensis was a truly unique creature, which could try out some new methods of movement, which would become much more developed only in true dinosaurs.
The identification of the new locality of Gondwanax paraisensis helps understand the processes that culminated in dinosaur evolution. Researching its features, researchers are able to learn more about what these animals may have been undergoing during the Triassic era, a climate that was considerably warmer than it is today and when the first true dinosaurs were first coming into existence.
Paleoenvironment
This area of the geologic subsurface is in the present southern Brazil belonged to the Gondwana during the Triassic time. They had a warmer environment, and the geographical formation was characterized by large flood basins and a number of rivers. Gondwanax paraisensis probably roamed these ancient terrains, coexisting with early mammals, turtles, frogs and other reptiles.
Research and Future Studies
Scientists are still studying the fossil evidence collected from the Gondwanax paraisensis site because new anatomical and other aspects concerning its life are still being discovered. Such other research questions may be on its diet, behaviour and the relationship it had with other species existing in its environment. These details are then collected in a way that can help researchers better understand the exact evolutionary lineages that produced the dominance of dinosaurs.
The first known sauropods Gondwanax paraisensis is one of the remarkable find of palaeontologists regarding evolution of the dinosaurs. The little reptile possessing some biomechanical characteristics can provide much information about the modifications and the developmental phases that took place during the Triassic age. Besides, new exploration is expected to go on, Gondwanax paraisensis will play an important role in elucidating the intricate and interesting history of the origin of life on the Earth.
Evolutionary Implications
The first time finds of earliest dinosaurs in Gondwanax paraisensis within southern Brazil, an aspect that can be considered a major breakthrough in rediscovering the emergence of dinosaurs on the face of the earth. Only growing up to one meter in length and had four legs, this reptile existed around about 237 million years ago when the first true dinosaur evolved. A discovered in Paraiso do Sul gives a clue to learn more about the evolutionary factors that led to dinosaurs.
Bridging Evolutionary Gaps
Gondwanax paraisensis is one of the oldest known members of the Silesauridae – reptilian fauna associated with dinosaurs. This species’ discovery aids our understanding of how one group of Earth’s first reptiles evolved into the first dinosaurs. It presents a more accurate information concerning the movement of species during the Triassic age, the manner in which the species transformed concerning physique and behaviour as they gave way to dinosaurs.
Anatomical Significance
The fossil of Gondwanax paraisensis witnessed consists of a part skeleton with right femur, cervical and dorsal vertebrae, sacral vertebrae and a part pelvic girdle. This indicates that Gondwanax paraisensis was still toying with methods of locomotion which would develop even further in the other dinosaurs. The light built body and long tail also suggest of mobility as well as flexibility that are critical competitive features to exist in a fluid habitat.
Evolutionary Experimentation
It is well demonstrated by Gondwanax paraisensis The Triassic period was marked by a burst of evolution, with different reptilian progeny experimenting with different morphologic and ethologic solutions. The new material from Gondwanax paraisensis contributes to the knowledge of the early dinosaur morphs’ ability to occupy various kinds of ecological niches. This flexibility would later define the dinosaur’s evolution enabling the animal to rule the land for millions of years.
Evolution of dinosaurs
The finding of Gondwanax paraisensis will forever change the manner in which future research is conducted and our future understanding of dinosaur evolution. In this way, analysing the details of its structure and comparing with other early dinosaur morphs we can recreate the chain of evolutionary changes that occurred at the beginning of the dinosaurian evolution. It also combining all significant changes like postural, locomotory, and feeding from an identification aspect that fashioned dinosaurs into being the leading terrestrial vertebrates throughout the Mesozoic age period.
Future Research Directions
This exciting discovery still continues with researchers dissecting the fossil of Gondwanax paraisensis to understand more about other aspects of its existence. Future studies may include what it ate, how it acted, and how it reacted to other such species within its habitat. Whereas such individual bits of data might at first seem too fragmented for any solid interpretation, if pieced together, they can be helpful in getting a clearer idea of the evolution scenarios which resulted in the dinosaurs’ ascendancy.
Conclusion
Gondwanax paraisensis, the newly recognized Triassic dinosaur from Patagonia, fills the gap in early dinosaur evolution and provides a unique opportunity to investigate the anatomical, ecological, and evolutionary changes of the dinosaurs in the middle of the Triassic. Its discovery also fills key gaps in the understanding of Early Mesozoic paleo-biology and evolution of dinosaurs, the group that includes early reptiles, crocodilians, and birds, underscoring importance of evolutionary testing of new designs in the history of life. Still more future research awaits and Gondwanax paraisensis will continue to enlighten the experiences in the convergence of the molecular and morphological diversification of different life forms on Earth.
What is Palaeontology?
Palaeontology is a branch of biology and earth science that deals with the manner and time in which animals and plants lived on earth. It is the branch of paleo-biology that includes the study of fossils, the organisms that they represent and the factors that have allowed their preservation over tens or hundreds of millions of years. Through studying fossils palaeontologists can explain how life used to be and how it has adapted and changed over millions of years on the Earth.
Core Objectives
- Understanding Evolution: This way, one of the mainscience objectives is to study how life has developed for millions of years.Through the analysis of the fossils, one can most importantly look at thephylogeny of the various animals or plants most important the evolution processand also relate the extinct species with the living ones.
- Reconstructing AncientEcosystems: Modern day palaeontologists work to reconstruct ecosystem in order to study howthe organisms of the past existed in that ecosystem. This means not only usingindividual fossils, but the matrix that contained them, the sedimentology ofthe surrounding rocks and geochemistry of the deposits.
- Interpreting EnvironmentalChanges: Byanalyzing the fossil records of ancient climatic conditions different changesin the weather can be ascertained. From studies conducted on fossils, climate,sea levels and composition of the atmosphere can be deduced and thus explainthe environment of the Earth.
Key Disciplines in Palaeontology
- Paleobotany: Paleobotany is the branch of botany cantered on the analysis of plant microfossils such as leaves, seeds, spores, pollens as well as macrofossils in form of wood. Paleobotanists study history of plants, and their role in the past worlds, including pre-Quaternary flora.
- Paleozoology: The study of trace remains, impressions or bubbles of preserved but not fully fossilized animals and their relation to the earth’s surface and land masses. It advances this field to reveal the richness and variability of animal life in the prehistoric world.
- Micropaleontology: The scientific analysis and identification of fossilized organisms under the microscope including the foraminifera test and the frustules of diatoms. Scientists study these microorganisms to understand the previous instances of sea climate and other conditions.
- Ichnology: Subdiscipline of paleobiology where scientists focus on direct evidence of past life which includes footprints, burrows and feeding tracks. Iconologists study these indirect clues of past life with a view to determining the behaviour and movements of the extinct species.
Methods and Techniques
Fossil research is carried out through field research, laboratory work and through the use of other techniques such as tomography. Field work is the process of prospecting, digging up fossils and fossil bearing sites and since fossils are rare and very valuable, the works involved here requires great respect and care with samples collected properly documented. Through lab work, fossils are washed and sorted with a calliper for size, or studied microscopically, scanned in CT scanners, or analyzed for isotopes to determine its age, structure or even chemical characteristics.
Significance of Paleontology
It then meant that paleontology was important in the study of the past but also important to the future. Paleontologists use knowledge of how life on our planet has adapted to previous climatic shifts to make recommendations and predictions of modern day problems such as global warming, environmental degradation, and stream conservation. Paleontology is to understand the complexity of interdependence in living organisms and the elaborated development of the world for billions of years.