The JD(U) promises support for the bill but expresses worry about methods to implement the "Waqf by user" clause on current Waqf properties.
Stakeholders across the board express strong disagreement about the Waqf Bill which approaches Parliament for enactment because it includes a retrospective part. Waqf Bill submitted to the Lok Sabha: Significant changes to the governance of Waqf properties in India are proposed by the Waqf (Amendment) Bill, 2025, which is scheduled to be tabled in the Lok Sabha. Important changes were made to improve administration while resolving issues made up in previous discussions. The core focus of this discussion features Waqf properties because they contain critical cultural values and vital religious aspects and notable historical importance. This legislation contains modifications which potentially shape how these properties are identified together with their management while triggering concerns about established sites facing legal disputes. Official statements about reform and efficiency coexist with on-going worries among political parties together with legal experts and minority representatives about the expansive scope of the retrospective provision.
Understanding Waqf and the 2025 amendment: Key reforms, challenges, and implications
The Waqf Bill serves as a crucial foundation for modifying how Indian authorities handle Waqf property management. The full appreciation of the Bill depends on knowing what Waqf is as well as all applicable conditions during its implementation.
What is waqf amendment bill?
The Waqf Amendment Bill 2025 aims to streamline the management of Waqf properties with provisions to safeguard heritage sites and promote social welfare. Through an Arabic origin meaning "dedicating or stopping use" Waqf establishes a system for donating properties or assets which function for various religious or charitable or educational purposes. The properties serve as references of perpetual possession and management for communal advantage that frequently enables vital support of foundational community spaces like mosques, establishments and cemeteries. Under the Waqf Act of 1995, Waqf properties generate religious sanctity and Waqf boards work under its authority to oversee them.
The Waqf Act, 1995
The administrators built the 1995 Act to make Waqf property management simpler through improved transparency and compliance. Every state required the existence of a Waqf board under this legislation to maintain property records and oversee property policies and resolve property issues. Waqf assets face inefficiencies in protection because of insufficient documentation, property infringement as well as a lack of contemporary management methods.
Proposed Amendments in the New Waqf Bill
The new Waqf Bill intends to remedy these issues through essential modifications which bring modern developmental aspects to the system. The Waqf by user provision has been eliminated from the new Waqf bill since it legitimized Waqf properties through their historical religious or community usage. The recent amendment about ownership and management seeks to clarify matters but it threatens existing Waqf designations when properties lack established documentation.
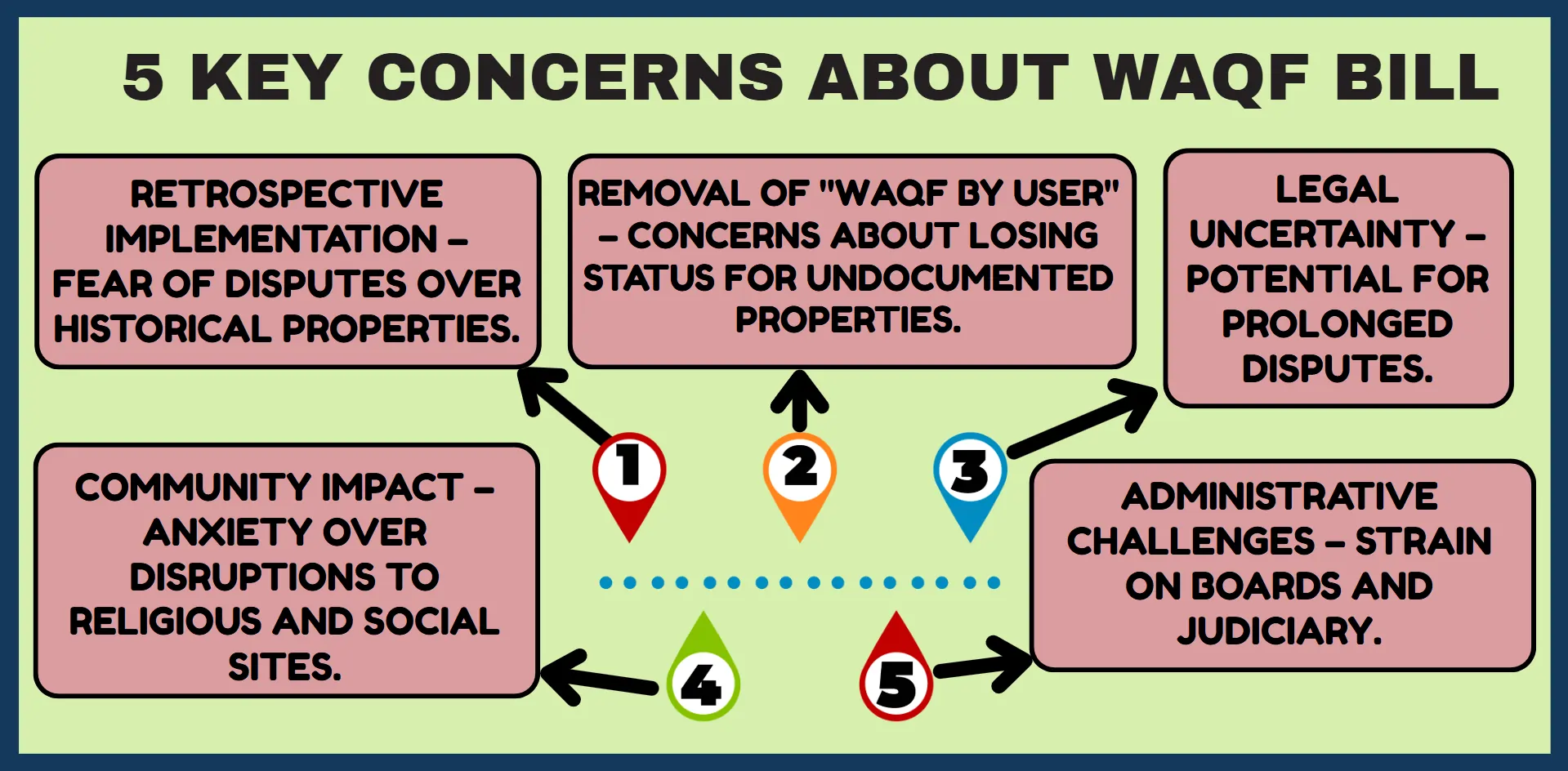
The bill proposes to make changes retroactively active which will affect all Waqf properties created before the bill became law. The past-oriented method of application has generated concerns by stakeholders because it could produce disagreements about property history usage. The critics believe that these provisions work against the fundamental characteristics of Waqf because they depend on uninterrupted continuity of historical developments.
The Concept of Retrospective Implementation
This legislative practice pertains to enforcing laws and regulations upon pre-implementation occurrences that exists before legislation passed. These legal provisions contrast with prospective laws because they assess previous events to potentially adjust their resulting effects. The occurrence of retrospective laws remains familiar but their execution commonly creates difficulties about maintaining fairness or predictability and altering settled matters.

The Waqf Bill faces significant opposition because of the proposed application of retrospective implementation. Under the proposed amendments of the Bill, legislators work to resolve on-going problems regarding Waqf property classification along with its management procedures. The "Waqf by user" provision will be totally eliminated from property recognition mechanisms by the proposed amendment. Retroactive enforcement of these changes risks losing Waqf status because insufficient records from the past cannot verify Waqf standing. The new amendments cause concern about property disputes that could emerge due to the evaluation of decades-long religious community-owned properties.
Transferring Wafq ownership with retrospective application becomes difficult when dealing with historical properties including Waqf properties. The determination of site usage and their historical or communal importance relies on traditional techniques that communities follow throughout time. When introducing new criteria after the fact it may damage current legal processes, create social instability and court-related difficulties.
Proponents of retrospective implementation maintain that such measures bring order to standards and they solve discrepancies in property classifications. Some opponents maintain that the policy destroys Legal Certainty because it makes people and communities doubt the laws actively in place during their period of governance.
Concerns Raised by Stakeholders
Different groups of stakeholders have raised extensive discussions concerning the Waqf Bill as it generates varied worries among political associations alongside minority communities along with legal professionals and civil society organizations. Stakeholders express their main reservations about the Waqf Bill because it applies retroactively and makes adjustments to Waqf property classification rules.
Political Parties’ Concerns
Opposition representatives and core backers of the governing party share misgivings about what the proposed Bill would bring. JD(U) and TDP have voiced their concern about the potential dispute over established Waqf properties because of the "Waqf by user" elimination together with retrospective application. Their argument suggests the amendments could damage historical sites which lead to unclear situations regarding property claims. Social and legal complications emerge because the opposition party asks for more transparent provisions.
Community and Religious Groups’ Fears
The main stakeholders in Waqf property matters ‘the Muslim community’ communicate its concerns that traditional Waqf practices may fall out of favour because of updated legislation. Traditional management practices have been used for recognizing many Waqf properties instead of formal record-keeping. Explorations to eliminate the "Waqf by user" clause risk reducing Waqf status from mosques, graveyards and important sites leading to community member frustration. The proposed retrospective changes create additional concerns due to their potential risks to physically significant religious and social locations.
Legal Experts’ Perspective
Legal specialists have pointed out specific difficulties regarding the implementation of provisions that affect past circumstances. Legal authorities warn about the negative impact of reassessing past Waqf property identifications as this process would cause heavy judicial burdens and complex administrative complications. Legal certainty which guarantees stable predictable laws faces serious threats because of this move leading to mass apprehension among communities. Research findings show that disagreements about ownership rights may deteriorate presently fragile ties between state authorities and minority populations.
Civil Society’s Call for Dialogue
Prior to implementing the Bill civil society organizations emphasize the need to conduct inclusive dialogue. Such experts advocate for property management reform in Waqf but they insist the evolution should respect the history of communities while preventing their marginalization. The recommended measures demand complete transparency concerning Waqf property protection along with safeguarding their perpetual continuity combined with respect for religious and cultural interests of affected stakeholders.
The various stakeholders' apprehension shows that the Waqf Bill requires detailed consideration to create appropriate reforms that neither breach social balance nor diminish historical preservation.
Government’s Response and Assurances
Government officials have dedicated their attention to settling the issues that exist within the Waqf Bill regarding its past provisions and property categorization methods. Authoritative figures have acknowledged the delicate nature of the matter while stating clearly that the proposed adjustments intend to create an efficient Waqf property management system free from fresh disputes.
Clarifications from Key Leaders
Ministers of Union and senior government officials maintain that the Bill contains measures to boost Waqf board leadership while protecting properties against mismanagement and encroachments. The government officials state that retrospective implementation exists to fix irregularities while standardizing procedures instead of disrupting established traditional behaviour. The government has introduced specific steps which aim to stop arbitrary Waqf property reclassification when documentation or due process requirements are not met.
Commitment to Community Welfare
The government declared its on-going dedication to maintaining the cultural value and historical importance of Waqf religious and social facilities. According to government officials the deletion of "Waqf by user" aids property acknowledgment procedures to achieve openness alongside accountability. Accorded protections by officials ensure minority groups will receive measures to defend religious and social sites from losing their Waqf status.

Technology and Modernization Efforts
As part of improving management practices the government intends to utilize technology-based solutions through digital recordkeeping and centralized database systems. The government has launched modern initiatives which work to increase transparency while minimizing disputes and making the administration of state Waqf boards more organized. Through newly proposed modifications the system contains conflict resolution methods which provide stakeholders with fair process access.
Through these statements the government demonstrates its approach to reconcile modern reform strategies with respect for cultural heritage alongside community needs. Waqf properties will benefit from dialogue-based measures which establish safeguards because they help stakeholders trust each other and overcome issues of inadequate management. Neutral implementation of these assurances will drive the realization of meaningful results.
Broader Implications of the Bill
Waqf Bill implementation carries important wider effects which surpass administrative and legal objectives by affecting social political forces and minority rights as well as governance structures. The proposed significant changes for Waqf property rules presented in the Bill aim to create a new balance between state and minority groups and shape how cultural and historical heritage is protected.
Impact on Minority Communities
Actual implementation of amendments continues to concern Muslim minority members who are essential Waqf stakeholders. Waqf institutions preserve foundation properties through which they operate both as public social centres and community welfare platforms that finance religious needs and education and charity. The government's alleged reduction of sacred status for historical properties would cause the public agencies to lose trust in religious communities and potentially trigger more societal unrest.
Challenges for Governance
Administration faces the dual task of modernizing governance systems and respecting historical legacies according to the provisions of this Bill. When applied retroactively the number of property status disputes will increase causing further strain on judicial institutions as well as administrative bodies. The development of digital records combined with standardization standards demands significant funding support along with combined efforts between Waqf boards with government agencies.
Political and Social Ramifications
The bill might create a major political conflict between opposing views about minority rights and secular control of public assets. Opposition parties use contentious elements in the legislation to mobilize their base from minority groups thus worsening the national political divide. Strategic provisions of the Bill have the potential to direct nationwide social dialogue about heritage protection in a modernizing India.
The Waqf Bill brings necessary property management changes yet its wide implications show that inclusive policies need to be developed carefully. Main barriers to reform implementation include achieving transparency combined with community defence and encouraging inclusive dialogue between stakeholders so reforms can proceed while maintaining a harmonious community environment.
Conclusion
Through the Waqf Bill the government makes its most substantial effort yet to update Waqf property management and classification systems while fixing ineffective governance issues. The Waqf Bill prompts widespread anxieties across all stakeholders that include political supporters and minority religious groups because of its implementation timeline and elimination of Waqf by user clause. Establishing harmony between modern reforms and preservation of historical and cultural values stands as an on-going dilemma. The legal framework of the Bill extends its effects into the realm of social cohesion between different groups while shaping how minorities trust the government. For the reforms to benefit all stakeholders while maintaining Waqf's core elements the implementation demands constructive dialogue together with transparent methods and inclusive policy-making.