
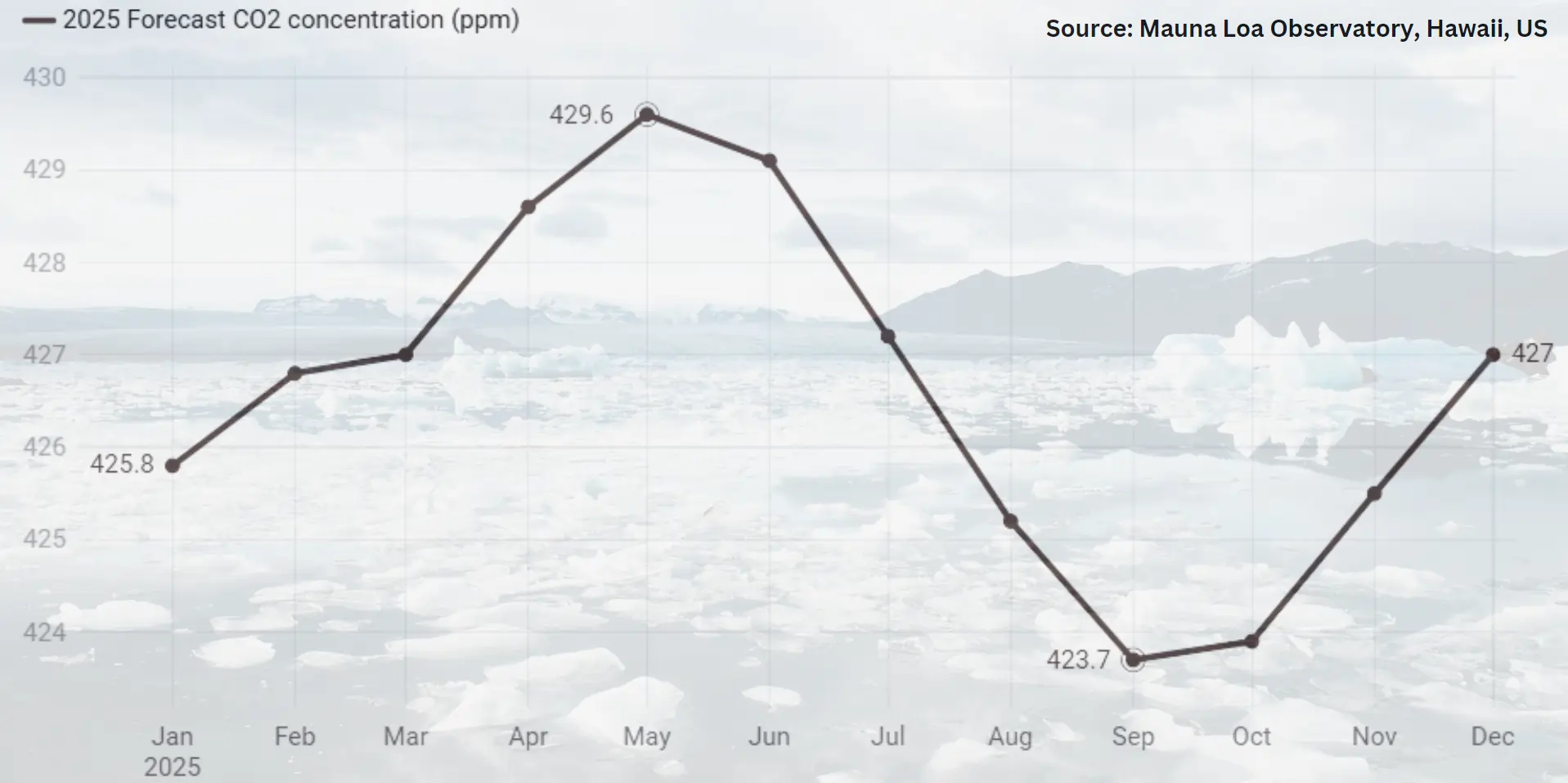
Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration in the atmosphere is expected to hit 429.6 parts per million (ppm) in May 2025. CO2 level at 415 ppm is the highest recorded in more than 2 million years and is a stage in the more profound climatic change.
Background and forecasts of the given period
Currently the Earth’s average concentration of CO2 is at 429.6 ppm the last time this level of CO2 was present in the atmosphere was during the Pliocene epoch which is roughly 2.6 to 5.3 million years ago. At this time period, global average temperatures were higher and sea levels were greatly higher than today. According to the current forecasts extrapolated from the Mauna Loa observatory in Hawaii, the level of CO2 will increase sharply due to record levels of fossil fuel use, as well as decreased CO2 absorption by natural sinks, and due to extensive emission of damage of large areas by wild fires.
Rise
Among the cause of the enormous increase in CO2 situation, the notable factors are; the main cause is the combustion of fossil fuels like the coal, oil and Natural gas pumps copious amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. Secondly, conversion of the forests to other land uses has decreased the size of or reduced the effectiveness of natural carbon reservoirs including the tropical forests. Many forests have also been burned out due to wild fires which are resultant of climate change and extreme weather condition, in the process large amount of carbon stocks have been emitted to the environment.
Implications
An increase in CO2 levels has direct consequences to the current global warming. CO2 is an greenhouse gas that has a direct impact of the earth’s temperature since it is known to cause heat tidal effects in the atmosphere. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has set the Paris Agreement goal at preventing the global average temperature from rising by 1.5° Celsius above the pre-industrial level. But the current trend of the carbon dioxide emissions per year is not suitable with the above goal, mainly because the annual emerging rate of CO2 remains to be higher than the sustainable rate of 1.5°C.
Challenges
Reducing the levels of CO2 emissions is always a great concern. Thus, to lower the degree of dependency on fossil fuels, their share needs to be replaced with renewable energy sources, including wind, solar and hydro power. This transition requires investment in the physical infrastructure, the technology, and the appropriate changes to policy. Furthermore, improving carbon capture and storage (CCS) can reduce CO2 emissions and they are however relatively more experimental.
International Actions and Policy Measures
Emissions of CO2 have been at the center of global coping measures including the Paris Accord where the world agreed to control the temperature increase. But, such efforts are only practical if the countries concerned pull out the stops. Other policy interventions like carbon pricing, subsidies to renewables, and restrictions on emissions constitute the mechanisms for transition to low carbon economy.
Carbon Dioxide Emissions: a global challenge and its negative effects
Carbon dioxide emissions have emerged as one of the biggest existing and unresolved problems on an international scale. Despite the fact that individual countries may release different volumes of CO2 to the atmosphere, the impact of the released emissions is worldwide. This, however, has consequences that touch on all spheres of life on the whole planet.
A Global Issue
Carbon dioxide is well known as one of the greenhouse gases which warm the Earth atmosphere and cause climate change. Carbon dioxide is emitted from fossil fuel use, deforestation and many other industrial processes. These activities are experienced in both the developed and developing countries so the emissions of CO2 are a worldwide problem.
Contributions from Different Countries
- Developed Nations: In the past, the developed countries are responsible for emitting high levels of CO2 to the atmosphere. First, the industrialized developed countries such as the United States, most European countries and recently the Canada have relied purely on the fossil fuels for industrialization and economic development collectively. While these nations are trying to cut emissions currently, their complete contributions to emissions are still high.
- Developing Nations: many emerging economies as China, India and Brazil are in the list of top CO2 emitters. Higher levels of industrialization, urbanization, and the growth in energy consumption in all these countries are responsible for the figures of CO2 emissions. Though, these nations are striving for sustainable development they are already emitting large amount of carbon.
International Cooperation and Policies:
Reducing CO2 emissions is only possible with the help of collective endeavour on the part of individual states and international organizations. International pacts like the Paris Accord seek to keep the global temperature rise below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. Nations are expected to apply obligatory emission reduction goals, increase the use of renewable energy, and improve the C storage capacity. But, to realize these objectives, international cooperation and undertakings are required from all the members of the international society.
Adverse Effects of Increase in Carbon Dioxide Levels
CO2 emissions increased in the last decades and have consequences on the environment, ecosystems, and human health. The following sections will explain some of the worst impacts associated with the elevated levels of CO2.
- Global Warming and Climate Change: The greenhouse effect; increased levels of CO2 cause an increase of global temperatures due to heat trapped by the atmosphere. Hence there will be an increase in world temperatures, melting of polar ice caps and consequently there will be an enhanced sea level. Most of the extreme and frequent weather conditions ranging from hurricanes, droughts, and floods bring enormous risks and negative impacts on communities and economies.
- Ocean Acidification: 70 percent of the human-caused CO2 emissions are dissolved by the seas in what is known as ocean acidification. This process brings down the pH in seawater and is not friendly to other forms of life in the sea. Mangrove and especially coral reefs, that are critical for marine ecosystems, are threatened by ocean acidification.
- Impacts on Ecosystems and Biodiversity: Higher temperatures as well as shifts in precipitation affect places, geological features and geographical areas. Changes in climate affect many plants and animals and their populations resulting in shifts in geographical distribution, decline in population numbers, and disappearances. Reductions in the number of species within an ecosystem compromise the comprehensive function of ecosystems cause failure to facilitate common life events such as purification of air, water and pollination.
- Human Health Risks: Various negative effects of climate change brought about by increased CO2 emission levels can be very harmful to human health. Higher temperatures and heat waves may cause heat disorders and heat fatalities. They still warned that changes in weather, particularly precipitation, increase the risk of vector-borne diseases including malaria and dengue fever. Moreover, it has effects on people’s physical well-being, which are injuries as well as displacements and mental health.
- Economic and Social Impacts: The economic impact of increased emission of CO2 is therefore severe. Floods and hurricanes that occasionally occur also contribute to a loss of property and a lot of damage to property. Weather instability has become problematic for agriculture, and that states food security is at risk. In this case, the social cost of global warming is felt mainly by vulnerable groups mainly those in the developing world increasing inequality and poverty.
How it can be reduced and Save the Earth
Greenhouse gases with special emphasis to the carbon dioxide gas (CO2) are the major cause of global warming and climate change. Sulphur oxide, nitrogen oxide and carbon oxide emissions should however be reduced in order to minimize their impact on the environment and future sustainability of the planet. In this part, measures or ways to cut down CO2 emissions and save our world are evidently described.
Renewable Energy Transitions
It is pointed out that for minimizing of CO2 emission the most efficient option is a shift from fossil fuels to renewable resources. Unlike coal, oil, and natural gas, the wind, solar, hydro, and geothermal power emit near-zero volumes of CO2. Both the government and industries must put their resources in renewable power systems and encourage the utilization of effective green energy systems. This also comprises of investing in large solar and wind prospects, investment in small-scale clean electricity projects for use in houses and companies.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Energy conservation in all systems and sectors is key to decreasing CO2 emissions dramatically. This entails using technologies and measures in power generation, in industries, transportation, and homes and offices. For example, proper use of light bulbs, fridges, air conditioning units, and other electronics in homes, can reduce energy usage. In the transport industry, adoption of efficient energy systems and market incentives for vehicle efficiency and use of public transport systems, bicycle, and walking can be some of ways of decreasing emissions. Businesses should reduce their energy consumptions through adopting minimized energy equipment and procedures.
Market development of EVs
CO2 emissions are significantly contributed by transport operations. Switching to EVs is a great way to cut the emissions from this sector. Governments can buy more EVs, subsidize their purchase, directly fund charging infrastructure and contribute to advancement of EV technology. Also, transit-oriented strategies such as encouraging the usage of public transport and promoting development of efficient mass rapids transport systems that can supplant private cars can also decrease the levels of CO2 emissions.
Reforestation and afforestation
Different forests are reservoirs of carbon dioxide – they absorb it from the atmosphere. Reforestation (growing trees on regions that used to be forests) and afforestation (growing trees on regions that have never been forested) can help remove CO2 and stop climate change. People and organisations should encourage planting of trees as well as avoid destruction of natural forests. Cities should also have more green coverage increasing the chances of quality air and reducing on effects such as the urban heat island effect.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Carbon capture and storage CCS technologies involve the confinement of the emission of carbon dioxide resulting from industrial activities and operations of power plants. The captured CO2 can then be transported to propose storage in various underground geological structures. The CCS technology is still in its infancy, as increased research and development investments bring CCS into the spotlight as a possible solution for lowering industrial emissions.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
CO2 emissions also come from agricultural activities which forms another important economic sector. Adoption to sustainable farming practice could be a realistic way of managing the emissions from the farming sector. Earth management practices that farmers use include conservation tillage, organic farming, conservation reserve, and crop residue management which improve the soil qualities and carbon stocks. Further, limiting the utilization of synthetic fertilizer and advocating for the less use of chemical farming can decrease emissions. It is understood that governments can play a special role of giving incentives to farmers for practicing sustainable agriculture practices and use of attractive policies for funding agricultural research.
Minimising waste and encouraging recycling
The emissions from landfill are CO2 and Methane which is a major contributor on greenhouse gas emissions. Policies encouraging minimization of wastes produced, and increased use of recyclable materials contribute to the achievement of lower emission in waste management. Comprehensive waste management options, the promotion of reusable products and the disposal of compostable products should help cut down on the amount of waste that ends up in the dumps. Local authorities and different organizations can also purchase technologies for utilization of waste, which are turned into energy.
Policy Cooperation and Putting into Practice
Mitigation of CO2 emissions is not an easy task because it should involve international commitment as well as the commitment of implementing sound policies. Treaties like the Paris Accord are important in setting the emission reduction goals and fostering global commitment. Regulations and targets must also be supported by governments to follow up with theories including carbon prices, emissions trading, and regulation of the industrial emissions. For efficient fight against climate change there is need for countries to work together in sharing information, technologies, and materials.
Cutting down on emission of carbon dioxide is required in order to save the Earth as well as have a better future. This is achievable through: embracing renewable energy; improving energy efficiency; encouraging electric cars, afforestation, advancing carbon capture plans, sustainable agriculture, minimizing wastage, and international cooperation. This calls for collaborative efforts, by governments, industries and the public as part of measures meant to secure the future of our planet.