Later this month ESA is launching the Biomass mission which will create global forest maps to show their environmental status and carbon dynamic changes.

The natural ecological system functions through forests and these forests serve as large oxygen stores together with carbon reservoirs supporting numerous plant and animal communities. The European Space Agency (ESA) understanding the necessity to track and understand forest health worldwide so they have prepared for the Biomass mission. This mission belongs to the Earth Explorer program as it plans to launch a next-generation P-band radar technology satellite. Biomass represents a system capable of measuring forest biomass and mapping three-dimensional structures which will deliver exceptional perspectives regarding carbon storage and ecological system transformations.
Biomass (Biomass Monitoring Mission for Carbon Assessment)
The Biomass mission makes ground-breaking progress in Earth observation because it establishes specific methods for worldwide forest monitoring.
Overview of the European Space Agency (ESA)
European Space Agency began operations in 1975 as the leading organization that conducts space exploration and Earth observation. Through its membership of 22 countries ESA pursues scientific development together with satellite research and climate science assessment work. The space discoveries of Copernicus and CryoSat beside others have delivered essential information about Earth's well-being and global warming effects to society.
The Earth Explorer Programme
To address leading environmental inquiries ESA developed the Earth Explorer program as an interagency initiative. Earth Explorer missions dedicate themselves to studying intricate Earth-based systems which include ice movements and ocean flow patterns. Two successful ESA missions under previous years were GOCE and SMOS which made important advances in scientific knowledge discovery.
Why Biomass?
The global carbon cycle heavily depends on forests because they store massive quantities of carbon which help control climate change impacts. Yet, deforestation and forest degradation pose substantial risks to this delicate balance. The essential requirement to determine forest biomass amounts along with understanding carbon sequestration needs prompted ESA to develop the Biomass mission. The satellite-based Biomass mission aims to solve root limitations of standard measurement methods while giving worldwide precise forest health data.

ESA maintains its pioneering role in climate science through the Biomass mission which makes the organization an important force in environmental protection efforts. The mission brings ground-breaking innovations toward reshaping our abilities to both monitor and protect essential global resources.
Objectives of the Biomass Mission
The European Space Agency's Biomass mission functions to resolve major knowledge deficits in forest science as well as climate change mitigation mechanisms. Objectives include.
- Mapping Global Forests: The creation of detailed accurate maps represents the main goal for this mission. Through its P-band radar technology the satellite can successfully see through dense forests to collect data about the forest structure. The ability to monitor inaccessible regions becomes crucial since tropical rainforests serve as essential elements for maintaining Earth's ecological stability.
- Measuring Above-Ground Biomass: Above-ground biomass refers to the entire mass of living vegetation that exists above Earth's surface and the mission intends to evaluate it across all global regions. Scientists extensively use the above-ground biomass measurement to evaluate forest carbon uptake capabilities because it shows forest health markers and helps forecast carbon cycle impacts. The collected information will allow policymakers to establish better conservation measures through specific tools.
- Research about Carbon Storage and Carbon Cycle: Natural forests act as essential carbon dioxide reservoirs which help cool down climate change through their carbon storage abilities. The collection of forest density measurements together with data about height and biomass through Biomass allows researchers to track carbon storage dynamics and release processes. The acquired information will strengthen climate models by boosting their ability to forecast environmental transformations.
- Supporting Global Research and Policy: The mission stands committed to developing international partnerships between scientists as well as researchers and policymakers. Biomass offers worldwide accessibility to its data to support different fields including ecology and climate science. The mission provides vital data that establishes guidelines for global organizations dealing with forest protection along with sustainability initiatives.
The Biomass mission protects forests worldwide by using advanced technology and complete data collection to fight climate change effectively.
Technical Features of the Biomass Satellite
The Biomass satellite represents a technological wonder from ESA that uses its top-tier radar and orbital advancements to transform forest and carbon system research.
P-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Technology
Biomass relies on P-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar technology as its main operational basis through the use of particular wavelengths for optimal forest assessment. The unique feature of P-band SAR distinguishes it from other radar systems through its ability to transmit signals through forest areas in order to collect sub-surface biomass information. The mission depends on this special capability for effective dense tropical forest observation since conventional observation methods become impractical in such exacting environmental conditions. The selected operational band enables researchers to collect precise universal biomass data at a detailed level.
Impressive Radar Antenna Design
The satellite holds a 12-meter radar antenna serving as the biggest antenna system for Earth observation which stands as its primary distinctive design aspect. The antenna maintains modern design principles that enable accurate forest biomass measurement detection at peak sensitivity parameters. Due to its large size the satellite performs full-scale mapping when it passes through wide areas. The satellite uses its cutting-edge, sophisticated antenna to carry out precise data collection operations.
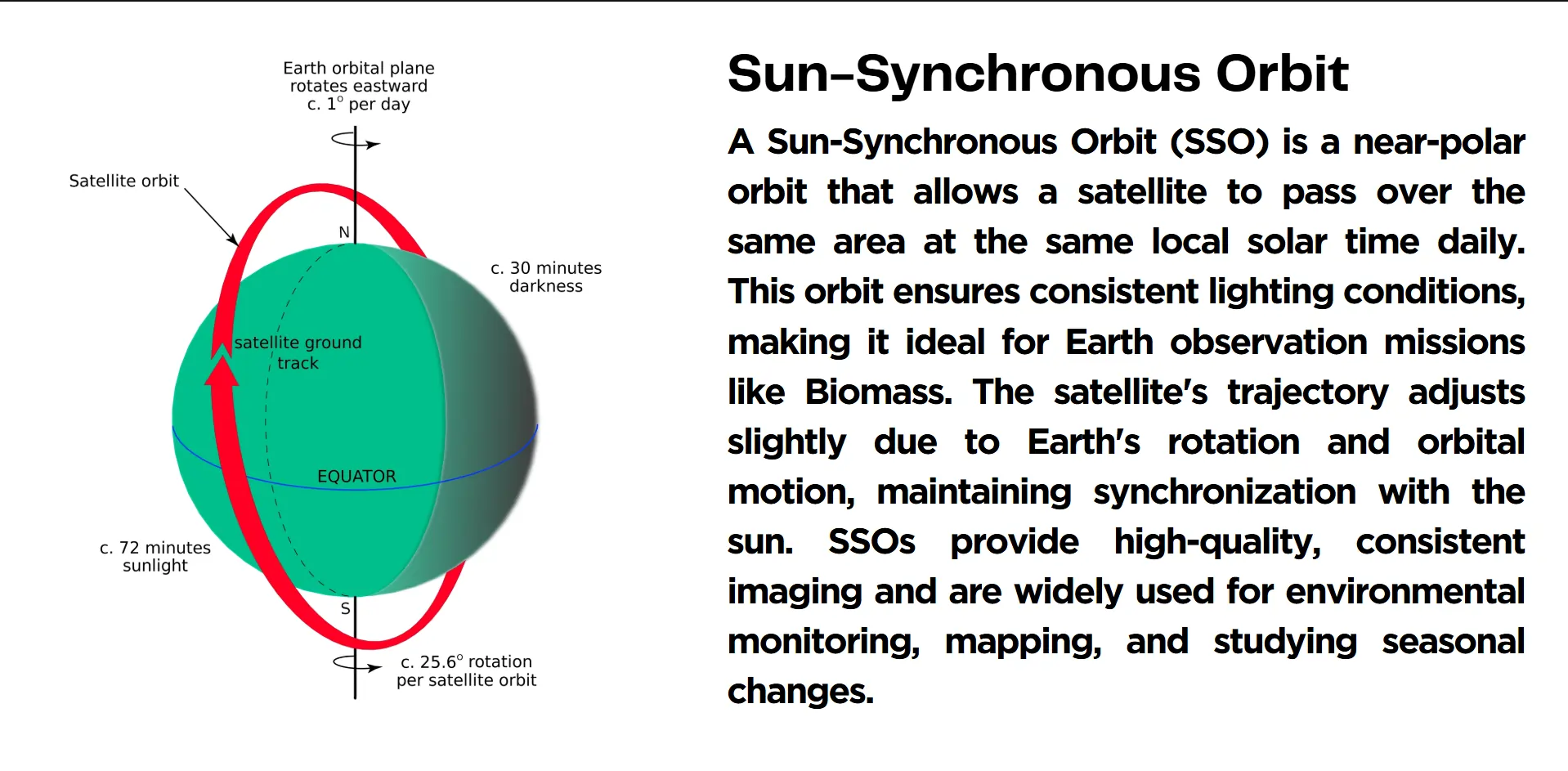
Sun-Synchronous Orbit
Because the sun-synchronous orbit of the Biomass satellite provides uniform light visibility for surveyed locations, it produces the best results. With this particular orbital setup the satellite can map identical solar time regions to obtain maximal forest observation data. The satellite reaches its ability to monitor forests worldwide by using its planned orbital pattern across diverse ecological settings.
Biomass satellite operation executes essential Earth observation due to its technical capabilities that will establish new methods for forest assessment in climate change mitigation efforts.
Expected Outcomes
The Biomass mission now has all the capabilities needed to deliver innovative insights regarding forest activities in climate change responses. Here's what to expect:
Enhanced Understanding of Forest Biomass
The main objective of this mission consists of acquiring worldwide extensive measurements of forest biomass. The Biomass satellite uses its radar system to measure forest dimensions for producing precise above-ground biomass and forest height information. Through acquired scientific data researchers obtain full visibility into which forests face deforestation risks so they can develop appropriate conservation strategies that match those locations. The gathered information provides the essential base knowledge needed for future forest observation systems.
Insights into Carbon Dynamics
Observations made by the satellite system will detect carbon cycles across areas which historically lacked valid data. Accurate understanding of these carbon dynamics proves essential for developing better estimates of carbon budgets as well as determining forest relevance to carbon sequestration. Climate models will receive helpful data that makes predictions better regarding environmental and global warming changes.

Global Collaboration in Research
International scientists , ecologists and policymakers will work together under this mission to achieve their goals. Biomass's public availability of its data will enable diverse research investigations including biodiversity tracking and land-use study. The combined research model works to enhance worldwide projects regarding forest protection and sustainable forest management systems.
Impact on Climate Policy
The data gathered through Biomass research will have substantial effects on worldwide climate regulations. Through its gathered data the mission will confirm the validity of carbon trading programs along with reforestation initiatives coupled with stronger legislation against deforestation.
Through these transformative outcomes the Biomass mission will enhance scientific discovery, protective forest measures and climate change response strategies.
Broader Implications
The Biomass mission extends scientific discovery to create significant effects for global climate research together with conservation initiatives and sustainable development throughout all regions.
Combating Deforestation ands Forest Degradation
The Biomass mission exhibits its fundamental importance through its capability of dealing with forest destruction and environmental damage. The satellite will deliver exact forest-health and structure information which allows policymakers to detect vulnerable regions so they can implement preventive protection measures. The implementation of proper protective measures through satellite data will reduce forest depletion rates thus maintaining forest biodiversity functions as well as their carbon capture abilities.
Shaping Climate Policy
The Biomass mission becomes a source of essential knowledge that serves as fundamental input for building worldwide climate policy structures. Nowadays nations use forest biomass observations along with carbon storage measurements to develop evidence-based approaches against climate change. Through this data governments create strong carbon trading operations while simultaneously developing forest restoration projects which help fulfil international climate agreement goals.
Advancing Global Collaboration
Open data exchange between academic subjects becomes feasible via this mission due to restricted access elimination. Scientists together with ecologists alongside worldwide organizations will use collected data to accomplish conservation work and initiate new research projects. Many organizations working collaboratively play a crucial role for solving large environmental problems around the planet while ensuring the development of standardized sustainability plans.
Driving Technological Innovation
The Biomass mission enables future Earth observation missions because it displays revolutionary radar technology and spacecraft design capabilities. A successful completion of this mission will motivate the creation of ground-breaking technology for ocean monitoring alongside urban sustainability research.
Worldwide environmental protection and climate change reduction depend heavily on the Biomass mission because it supports strong forest ecosystem research initiatives.
Challenges and Limitations
The Biomass mission demonstrates remarkable capabilities for enhancing climate science research and forest observation though various obstacles remain before operational readiness. The forthcoming section analyses potential obstacles which might threaten the mission.
- Technical Challenges: There is no way for the Biomass mission with its P-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) technology to avoid operational restrictions in spite of its advanced capabilities. Data accuracy recorded by P-band range radio frequency signals from external sources might become incorrect. For the satellite to work at its optimal level scientists need to monitor its continuous calibration throughout the entire operational period. Regular technical checks of the satellite are necessary for optimal operation under varying space environments.
- Data Interpretation Complexities: The process faces an extra challenge when analyzing data received from satellite systems. Advanced amounts of information acquired from the Biomass mission demand both comprehensive processing steps and validation procedures. Soil moisture variation together with atmospheric interference is responsible for most unexplained changes in data measurement. Multiple scientific experts will have to collaborate intensely for applying this data to obtain real-world modelling outcomes with accurate results.
- Operational Limitations: The sun-synchronous orbit used by the mission delivers consistent lighting but it restricts the available mission operations. Linear capabilities of the satellite become restricted because repeated visits to certain locations might be inadequate to detect quick forest alterations together with short-term incidents such as unlawful logging. The satellite limitation in providing below-ground carbon data concerning root biomass and below-ground carbon storage necessitates a lack of total forest carbon dynamics understanding.
- Broader Impacts: The conversion of satellite-derived information into suitable policy guidelines might encounter delays in the implementation process. Transporting scientific findings into effective conservation practices confronts various barriers involving state policies and financial support and operational priorities.
The Biomass mission stands as an essential space initiative because it expands Earth observation science boundaries in spite of formidable challenges.
Conclusion
A landmark breakthrough in forest observation and climate monitoring emerges through the Biomass mission of the European Space Agency. This satellite utilizes advanced P-band radar technology to deliver innovative information about forest ecological condition and carbon reservoir status together with carbon cycle behaviour. The mission strives to strengthen conservation activities and at the same time guide international climate policy frameworks and build worldwide cooperative partnerships. The mission will have a major impact on environmental sustainability while driving technological innovation despite facing its fair share of challenges. Through the Biomass mission scientists display how forests play an essential part in fighting climate change thus encouraging people to make forest preservation their top priority for achieving a sustainable and sturdy planet.