
The Swachh Bharat Mission Urban 2.0 was further launched in the year 2021; it is the rebirth and enlargement of the first Swachh Bharat Mission started in the year 2014. This massive plan is intended to free the urban India from garbage and implement hygiene public sanitation principles. Understanding the SBM Urban 2.0, it might be said that this mission is not only related to cleanliness, but to the improvement of living conditions in urban areas and overall healthier environment enhancement.
The Vision and Objectives
The goal of the SBM Urban 2.0 is to build cities that are better managed with the waste. This includes Source segregation of wastes, effective and proper collection and transportation of the wastes and scientific disposal of wastes. The mission also has aspects concerning grey and black water management for achieving ODF+ (Open Defecation Free) status of all the urban local bodies with many going to ODF++.
Key Components and Strategies
- Waste Management: In this case, SBM Urban 2.0 is aimed at the entire chain of waste disposal. High level includes Collection of wastes directly from the source or households, source separation and provision of structures to provide waste management facilities. The mission advances shifting towards the use of technology and innovation in improving the efficiency of waste management. For example, there are plans to establish facilities for waste to energy that will transform RDF (Refuse-derived fuels) into energy.
- Legacy Waste Remediation: One of the core issues discussed by SBM Urban 2.0 is how to deal with the existing waste dumpsites. These and other sites which have received wastes over the years present serious environmental and health hazards. Through the mission, it is planned to rehabilitate about 2,400 legacy landfills by 2025-2026 while turning waste into bio-soil and construction scraps/recycled materials.
- Behavioural Change and Citizen Engagement: Another core concept of the new approach of SBM Urban 2.0, this concern is the engagement and the sense of ownership within the society. It also forms part of the mission which is informing the public and incorporating them in publicity campaigns for clean India and waste management. Take for instance the “Swachhata HaeSeva” that mobilises millions of citizens across the country for Swachhata activities.
- Digital Innovations: With the increasing use of the technology there is always a increasing tech solutions in the problems as in this case here SBM 2.0 has strategically involved the Technology in the mission plan. Mobile applications and web-based tools are employed for tracking and reporting on performance as well as for the communication with the citizenry. The Swachh Survekshan is an annual competition in which cities are ranked on parameters of cleanliness and sanitation where the digital tools assist urban local bodies to compete.
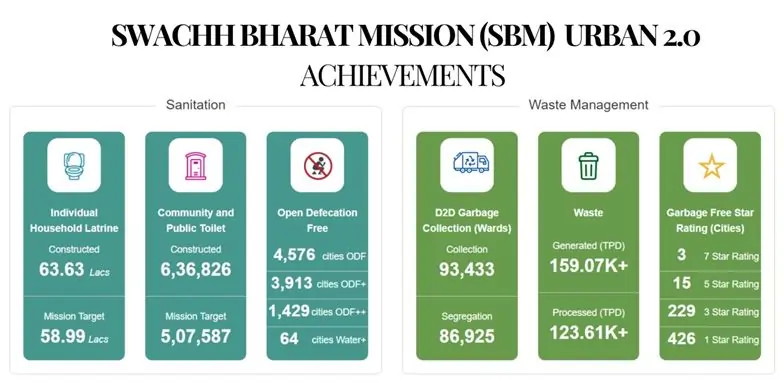
Impact
SBM Urban 2.0 has broken a number of barriers that have contributed positively to sanitation and waste management in urban settings. A lot of the cities have registered impressive strides towards the journey of the no garbage city and the improvement of sanitation. For instance, Ahmedabad has made a success story in emptying a conventional landfill site where it has developed an ecological park. Likewise, Nagpur has cleaned a 35-acre landfill to establish the possibilities of the urban renewal using an efficient waste management system.The mission has similarly transformed public and health and clinical cleanliness. SBM Urban 2.0 has ensured that there is minimal Undisclosed Territorial Repertory and better availability of toilets and washing stations for women and growth part, through the construction of the individual household latrine and community toilet. This has been realized through improved health and quality life among millions of population living in urban areas.
Challenge in urban waste management in India
Issues of waste management in Indian urban area are a concern for better future. Population growth and increased urbanization put a lot of pressure in the exponential rates in waste produced compared to capacity for waste management.However, challenges are present in SBM Urban 2.0 implementation programme too. The general level of waste production especially in city centres alongside the perceived need for change of attitude on the part of the citizens is a continuous process that demands optimal efforts and financial backing. Further, the mission should recognise the challenges of the financial and technical capacities of the smaller urban local bodies and some of the more concerns should be addressed as mentioned below:
- Inadequate Waste Collection and Segregation: Currently, there are few effective waste management and disposal services in most urban centres. About 70% is collected and then only a proportion of it is sourced to be recycled them. This results in what is referred to as mixed waste making recycling and processing all the more challenging.
- Insufficient Infrastructure: The infrastructure for wastes processing and disposal is usually poorly developed. Most of the cities use old fashioned landfills, which are ill-equipped to cope with the current level and nature of waste disposal. This leads to pollution of the environment and the generation of health risks.
- Public Awareness and Participation: Lack of awareness and little public involvement can be seen as the major problem concerning proper waste management. These range from segregation and recycling of wastes, to minimization of waste production.
- Financial and Technical Constraints: Many small urban local body executive and technical teams are poorly endowed in terms of funding and human capital to apply sound and sustainable waste disposal measures.
SBM Urban 2.0 Solutions
To surmount these challenges it will require continuation of innovation and flexibility on the part of SBM Urban 2.0. The mission can be conceived virtually, increasing cooperation with the private sector, expanding programs for building the capacity of organizations, and utilising best practices learned from other countries. Moreover, the process must be monitored and evaluated constantly to make sure that the mission properly steer the organization toward the outcomes required. So here the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) Urban 2.0 aims to address these challenges through a comprehensive and multi-faceted approach:
- Enhanced Waste Management Systems: SBM Urban 2.0 advocates the formation of effective waste collection, segregation, and special processing. This includes establishment of waste to energy plants and a material recovery facilities needed for processing different types of wastes.
- Legacy Waste Remediation: Better described as “best from waste”, the mission is to clear legacy waste dumpsites with resultant waste turned to bio-soil and recycled construction materials. First, it decreases pollution of the environment, and second, it helps to bring back the scarce space in urban areas.
- Behavioural Change Initiatives: Outreach activities as well as citizen participation initiatives are part of SBM Urban 2.0. These motions are appropriate to enhance an understanding and involvement of people within the waste management procedures.
- Technological Innovations: The mission utilises computers, internet and mobile applications for following up the progresses, incidents and civic interactions. This includes the Swachh Survekshan that is an annual survey that compares the cleanliness levels of cities.
Through these and other such hurdles, SBM Urban 2.0 is implementing smart urban sustainable solutions for a healthier urban India.
Outcomes of Swachh Bharat Mission Urban 2.0
The SBM Urban 2.0, commenced in 2021, takes us to a broader understanding of sanitation and waste management reforms in the urban environment of India. This mission, enhancing the impact of its predecessor, has developed significant accomplishments showing the long-term large-scaled scope of actions and focus on developing cleaner and healthier urban environment.
Improved Systems on Waste Disposal
It also stands out that SBM Urban 2.0 has implemented high-performing mechanisms of waste disposal both in the environment and within residential buildings. The essentials of the mission have included door-to-door waste collection that is now offered in a number of cities, thereby promoting source separation. This has made recycling and processing of wastes to be on the high side hence cutting down the amount that actually finds its way to the landfills. This tech is very useful in converting the waste into usable energy fuel.
Legacy Waste Remediation
On the question of legacy waste, SBM Urban 2.0 has recorded tremendous improvement. This mission has focused on some of the foul smelling grounds and turned them into useful ones. For instance, there has been successful rectification of the Bhalswa landfill in Delhi besides receiving the value of urban land; environmental concerns related to these dumps are also tackled. This has provided The National Cities with hope as they set on this same model as the reference to emulate in updating its waste management systems.
Better Sanitation System
There has also been improvement in the sanitation facilities in urban areas as a goal of the mission. The use of the household toilets and Community Toilets has reduced the cases of open defecation for inhabitants of urban areas. This has a positive effect on the health of the community especially the female and socially secluded groups through provision of proper sanitation.Citieslike Indore and Surat had been awarded for their exemplary sanitation practices. They have set such benchmarks that can inspire others too.
Civil Society and Human Behaviour
The string demonstration of SBM Urban 2.0 is the positive involvement of citizens in cleanliness. The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan not only being an elaborate communication campaign but also has acted through Swachh Survekshan survey as a great way of bringing responsibility and ownership among the citizens of this country’s urban centres. Both citizens and stakeholders have followed cleanliness drives and practical waste management to make the mission a long-term success story.
Technological Integration
Another success of SBM Urban 2.0 has been the success of integrating technology into their operations. States have used various online tools and mobile applications to track the progress, make reports on problems, as well as involve citizens. These digital tools have been used in the Swachh Survekshan survey, which rates cities and the urban local bodies’ cleanliness and sanitation performance, to enhance the competition and encourage improvement.

Therefore, SBM Urban 2.0 unveiled excellent advancement in shaping India’s sanitation and waste management landscape for urban areas. These accomplishments show that the mission has been successful and broad and spans across waste management, legacy waste, sanitation systems, citizens, and technology. As India goes steadfast in developing a garbage-free nation, SBM Urban 2.0 proves valuable for reminding people of the triumphs of unity with the goal of better health contributing to the future society.