
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus which is relatively new in the world and is rapidly turning into a major problem in china. First documented in 2001, HMPV belongs to the Paramyxoviridae family, which includes RSV, measles, and mumps. This virus predominantly infects the respiratory system and may lead to mild illness comparable with influenza. Yet it can cause more dangerous diseases like bronchitis and pneumonia especially in children under five, the elderly and those with other underlying health conditions.
HMPV mostly causes signs and symptoms that are similar to those of flu, which include coughing, runny or blocked nose, sore throat, fever, and wheezing. HMPV incubation period lasts about 3-6 days, although majority of the affected person only experience mild flu like symptoms that do not require any medical intervention, some people develop complications that warrant medical attention and treatment. The virus spreads through respiratory droplets from coughing and sneezing, direct contact with infected individuals, or by touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the face.
The researcher notes that over the past few months, there have been increased incidences of respiratory diseases, including HMPV in China. The health authorities in China recently observed that HMPV cases are on the rise mainly affecting kids below 14 years. New cases have been rising, so there are doubts about the possibility of further spread, as during the first wave of the COVID-19 threat. Images of crowded hospitals and people wearing masks have evoked memories of the global health crisis caused by COVID-19.
The appearance of HMPV in China has caused neighbours and international health organizations to tread carefully. For instance, India has its people adapt to high levels of alertness recommending that they wear face masks, wash hands frequently, and avoid touching their face among others. The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization have been watching it but the situation has not been labelled as an emergency or a crisis by WHO.
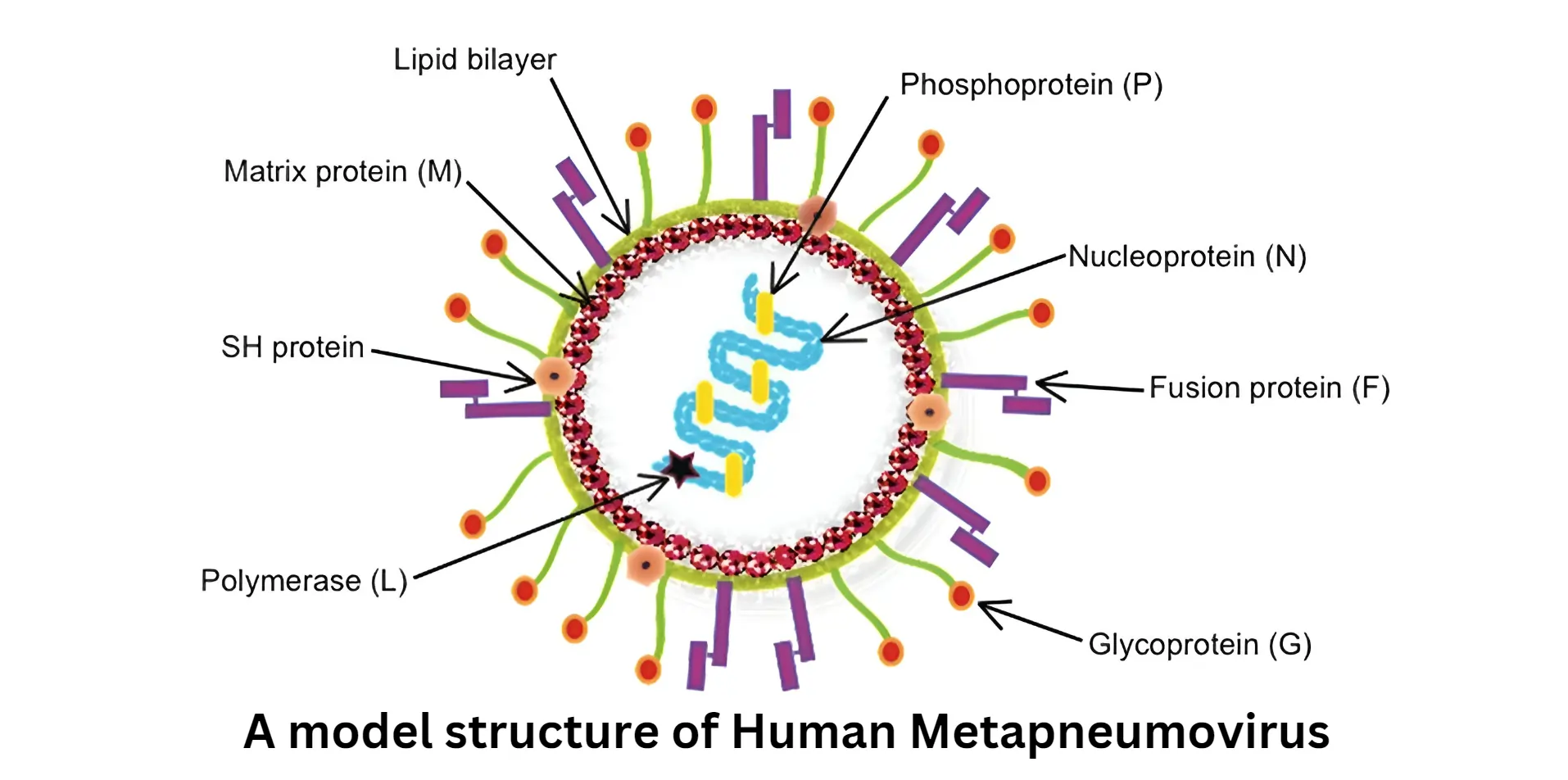
Further, it targets the high-risk population of the population such as; children, elderly people, as well as people with weak immunity. These populations also experience more severe, and sometimes life-threatening, illnesses such respiratory illnesses including bronchitis and pneumonia. Vulnerable populations should take extra precautions as the virus triggers respiratory illnesses as a complicating factor for existing conditions.
HMPV Symptoms and High Risk Population
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a newcomer of the family of respiratory viruses; it was discovered in 2001. It mainly involves the respiratory tract and can produce symptoms as those of a cold or flu. However, sometimes it causes more serious lung illnesses including bronchiolitis or pneumonia in children as well as other fragile persons.
Symptoms of HMPV
HMPV has relatively mild symptoms that might resemble those of other simple respiratory illnesses and ailments. Key symptoms:
- Cough: Usually recur and occupied a spectrum of disease severity from moderate to severe forms.
- Runny Nose: An often easily observed marker of the upper respiratory tract engagement.
- Nasal Congestion: This leads to breathe with difficulty.
- Sore Throat: Sometimes associated with pain and itching.
- Fever: Usually found in the early course of the infection.
- Shortness of Breath: Possible complications, where people might experience breathing problems include the elderly persons and any person having a pre-existing lung disorder.
- Wheezing: Indicative of constriction of the bronchi, closely related to serious problems with oxygenation.
- Fatigue: Common flu like symptoms such as fatigue and weakness.
In more complicated cases HMPV can cause complications like bronchiolitis or pneumonia especially affecting young children, the elderly or those with compromised immune systems.
Vulnerable Groups
HMPV affects some people more than others as some are immune-compromised or have some health complications that lead to heart failure or other complications. These vulnerable groups include:
- Young Children: Severe respiratory illness due to HMPV infection is more severe among infants and young children susceptible to be below five years of age.
- Older Adults: HMPV is also more serious for the elderly especially those aged 65 years and above.
- Immuno-compromised Individuals: Severe HMPV infections mostly affect those with compromised immune response due to medical conditions, cancer, or HIV/AIDS, use of chemotherapy, or immunosuppressive drugs.
- Individuals with Pre-existing Respiratory Conditions: Patients with a compromised respiratory system due to asthma, COPD or any other lung illness are particularly at the high risk of worsening symptoms from HMPV.
HMPV and COVID-19 are both respiratory viruses caused by enveloped viruses that are similar to each other as well as different.
Similarities:
- Transmission: At the same time, HMPV and COVID-19 infect via droplets through the air when an affected individual speaks, coughs or sneezes. They can also transmit by contact with contaminated surfaces and then touching the face.
- Symptoms: Both viruses present respiratory syndromes that include coughing, fever, nasal congestion, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, they may cause other severe lung diseases like pneumonia that require hospitalization.
- High-Risk Groups: Furthermore, both viruses are particularly dangerous to fragile people, including kids and seniors or those with a compromised immune system.
Differences:
- Severity: COVID-19 is more vicious and has a higher death rate than HMPV. HMPV is associated with severe respiratory disease but is typically less severe and much less fatal.
- Vaccination: Unlike COVID-19, there at the moment is no vaccine for HMPV, though several COVID-19 vaccines exist. Vaccinations have cut the effects of COVID-19 in various parts of the world due to the increasing availability of vaccines.
- Public Health Response: COVID-19 measures included lock downs, restrictions of movement and a myriad of massive health interventions all over the world. HMPV, on the other hand, has not necessitated such drastic measures.
Anticipatory Steps to Minimize Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that predominantly impacts the respiratory system, resulting in ailments akin to those caused by the common cold. It is widespread to all ages, but it is most dangerous to young children, people above 65 years, and people with a weak immune system. Prevention is always the best remedy to defeating an illness and this is not any different to HMPV; like many other viral diseases. Below are more effective prevention measures:
Personal Hygiene
- Hand Hygiene: The most effective measure practiced when handling HMPV includes washing the hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. If washing with soap and water is not possible include a hand rub using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer that has at least 60% alcohol. It’s crucial to wash hands:
- Before consuming or handling any form of food
- After using the restroom
- Every time you blow your nose, cough, or sneeze
- Each time one comes into contact with high risk contact surfaces such include doors, light switches and handrails
- Avoid Touching Face: HMPV can get into your body through the eyes as well as the nose and mouth. Do not touch your face with your hands especially when you have not washed them to prevent getting infected.
Respiratory Etiquette
- Cover Coughs and Sneezes: Cough or sneeze on a tissue, then throw the tissue away, or use the inside part of your elbow if nothing is available around. Immediately after using the tissue, discard it, and wash your hands with water and soap or use an alcohol base sanitizer. It can reduce the likelihood of one emitting the virus’s respiratory droplets onto objects, surfaces, and persons.
- Mask-Wearing: Masking the face when in crowded or enclosed environment can greatly minimize the spread of respiratory viruses such as HMPV. Masks prevent droplets from body and individual’s respiratory system from spreading to the environment and to other people.
Environmental Cleanliness
- Disinfecting Surfaces: Always ensure that the areas that are touched often with hands are washed or disinfected; this includes door handles, switches, countertop and phone. It is required to clean with approved disinfectants for viruses to guarantee security.
- Ventilation: To enhance indoor ventilation one must open both the windows and doors to allow fresh air into the room. Good airflow helps in reduction of viral concentration within the buildings.
Health Practices
- Healthy Lifestyle: Practicing a healthy civilized life increases the ability of your immune system to combat infections than an unhealthy life style. This includes:
- Consuming the right type of food and taking a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables and whole grains
- Getting regular exercise
- Staying hydrated
- Ensuring adequate sleep
- Abstaining from smoking tobacco and taking large quantities of alcohol.
- Vaccination: Although there is not a vaccine for HMPV you should stay current with your vaccinations and receive a yearly flu vaccine, as it may result in a respiratory illness which will weaken your immune system.
Community Measures
- Social Distancing: Avoiding close contact with others during social activities, while in crowded or confined places, can minimize the spread of the virus. Do not associate with or touch people who have cold or any sicknesses.
- Isolation and Quarantine: However, if a person within the household displays symptoms of HMPV, they should avoid contact with others within the house, to avoid transmission of the disease. Avoid contact with others and adhere to guidelines from the health professionals if the symptoms get worse.
- Public Health Awareness: Stay informed about HMPV and other respiratory illnesses through reputable sources such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In fact, increasing awareness and encouraging the adoption of preventer issues is possible by conducting campaigns and education among the public.
Special Considerations for Vulnerable Populations
- Protecting the Vulnerable: All households should ensure they take enhanced precaution to shield the young kids, the senior persons and all those with other forms of illnesses. This includes a number implementing and adhering to hygiene measures, refraining from going to ill frequent crowded areas, and regularly checking for the first symptom of respiratory disease.