
India, being a fast urbanizing and industrializing country, is grappling with various challenges on the proper management of wastes. Due to a rapidly growing population base and other corresponding economic activities, there has been exponential growth in the generation of wastes that act as sources of environmental, socioeconomic and economic concerns. There is one solution which has the potential to alleviate all the above mentioned problems and it consist in the implementation of the waste to energy (WtE) concept, which not only solve the waste management problem but also utilize the waste as a source of energy. This Article aims at discussing wastage production in India technology overview, benefits and risks and the way forward on how to tap into wastage production for growth and development.
Waste management technology
Waste-to-energy means the conversion of waste products into useful energy forms like electricity, heat and fuel etc. This approach also serves the purpose of waste management as well as energy generation hence the need to minimize the use of fossil energy. The potential benefits of waste-to-energy in India are manifold:
- Waste Reduction: Based on the use of WTE technologies, it is possible to discharge lesser amount of waste into the landfills. This is especially so for a country such as India that has dearth of space for new dumping sites and the ones that existed are mal-governed and saturated.
- Energy Generation: This means that WTE plants can produce electricity and heat from waste, thus meeting some fraction of the country’s energy demand. This is especially helpful in a country that uses a lot of energy and in a quest to innovate more sources of energy.
- Environmental Benefits: The use of waste to energy plants can finally provide a solution for waste disposal, were the waste has a destructive effect on the environment. They cut greenhouse gas emissions as they discourage methane formation in landfills and provide cleaner energy than coal-fired power plants.
- Resource Recovery: Moreover, WTE processes can extract metals from waste streams thus improving; the efficiency of resource utilization in accordance with circular economy principles.
Current Trend in Waste Management in India
India produces about 62 million tonnes of municipal solid waste (MSW) per year and urban areas have a high proportion of this waste. Regrettably, the trash indicated is collected with only 75-80% efficiency while not more than 25% is processed or treated. The rest finds its way to landfills hence posing serious environmental and health challenges including water and air pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.Conventional waste disposal practices like landfilling and open dumping are hence becoming less sustainable because of withdrawal of dumping sites and more to the undesirable environmental effects. Certainly, environmentally friendly waste management solutions are needed, and one of the best technologies for this purpose is waste to energy.
An Overview of Waste-to-Energy Technology
Waste-to-energy technology, also referred to as WtE, is a method of converting waste materials into fuel, power, or heat. The key approaches employed in WtE are:
- Incineration: The burning of waste where by waste material is incinerated at a very high temperature whereby heat thus produced can be used to make steam and generate electricity. Incineration has the advantage of minimizing the physical space occupied by waste in that it greatly reduces the volume of waste; there is however the emission problem which must be well dealt with.
- Anaerobic Digestion: The controlled bacterial reduction of organic matter at a lowered oxygen level to yield biogas (which consists of methane and carbon dioxide) and digest (fertiliser by-product). Biogas on the other side can be exploited for energy production while digestate on the other side can be used as a fertilizer.
- Gasification: The chemical transformation of organic or fossil-based carbonaceous materials into syngas a combination of hydrogen, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide by partial oxidation at high temperature.
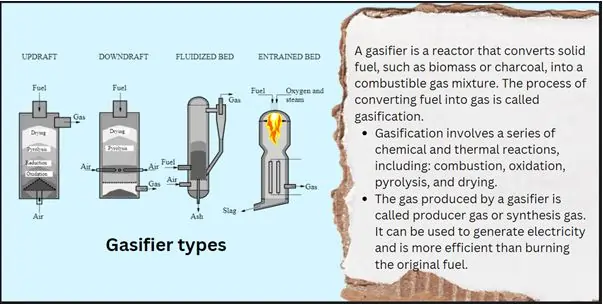
- Pyrolysis: Pyrolysis is the thermal degradation of organic matter in the no presence of any oxidizing element and produces bio-oil, syngas, and desired char. These products can be also employed as fuel or a raw material for undergone chemical transformations.
Advantages of Waste to Energy Technology
- Sustainable Waste Management: WtE technology can be seen offering a proper solution due to proper management of waste for disposal in landfills. From the fact that waste is being turned to energy, it also assists in proper disposal of wastes and hence eliminates the impacts of the normal methods of waste disposal.
- Energy Generation: WtE plants produce electrical energy that supplements the national electricity supply and diminishes the consumption of conventional power sources.
- Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions: When well operated, WtE plants emit less greenhouse gases than landfilling because the latter one releases methane, an undesirable greenhouse gas. Yet, using captured methane from the anaerobic digestion process in WtE technology, has substantial net positive benefits that can help mitigate climate change.
- Resource Recovery: Beneficial outputs from WtE processes consist of biogas, bio-oil, and digestate as obtained through anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis. They can be utilized for power generation, agriculture purposes such as adding nutrients in soil and much further usage in industries.
- Economic Benefits: WtE projects cause employment in waste management and the development of the renewable energy industry. Besides, it can mobilise investments and thus contribute to the development of the economy due to the emphasis on the circular economy.
Several difficulties that need to be addressed when implementing waste to energy projects
- High Initial Costs: The formation of WtE plants entails large capital outlay, which poses a challenge to the implementation by Municipalities and private players. Financing and the ability to guarantee that projects will be financially viable are other important issues.
- Technological and Operational Challenges: WtE technologies are sensitive to infrastructural provisions and operational and maintenance skills than other waste management technologies. The processes of providing consistent waste quality, controlling emissions, and effectively reusing energy are challenging.
- Regulatory and Policy Issues: WtE projects require policies and regulations that support it. They also include weak policies and laws, sleight regulations and policies, administrative bottlenecks, and vague policies that may hamper the WtE projects.
- Public Acceptance: Perceived pollution and health effects associated with WtE facilities are a major drawback, and public resistance to the establishment of WtE plants is always a concern. Developing and raising people’s concern through information sharing and group discussion is important.
- Waste Segregation and Collection: Collection at the source of wastes as well as collection systems in general are important determinants to the success of WtE projects. The failure by plants to effectively manage waste has an impact on the quality and quantity of feed stock needed by WtE plants.
Strategies for the Exploitation of Waste-to-Energy for Sustainable Development
However, to address the challenges related with WtE in India, a trans-disciplinary strategy is required. Here are some potential ways forward:
1. Analysingthe Policy And Regulatory Environment
- Enhanced Policies: The government should therefore come up and incorporate sound policies and legislation that enhance the establishment and development of WtE projects. This includes clear indication of how wastes are to be sorted, disposed, and treated.
- Incentives and Subsidies: Economic barriers can be addressed by providing monetary sweeteners for capital cost and subsidies for the cost of waste disposal for technologies employed in WtE. This can take the form of concessional tax policy, give-away grants and concessional credit for WtE projects.
2. Technological Advancements
- Adoption of Advanced Technologies: Hence, application of some of these emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning can enhance waste collection as well as treatment. AI systems has the potential of increasing efficiency of waste collection by optimizing route planning, increasing effectiveness of sorting processes as well as decreasing level of human interference.
- Research and Development: Development expenditure in WtE technologies is an area that reveals much for improvement and should therefore be encouraged. This includes better ways of improving the efficiency and decreasing the cost of converting waste into energy as well as recognizing better feed stock.
3. Public Awareness and Participation
- Community Engagement: Waste source management enhanced through public participation and awareness increase the level of waste segregation. Community programs and awareness campaigns make people use their services and support recycling and waste reduction services.
- Public-Private Partnerships: The use of WtE projects can be received with the help of a private sector that can provide experience, equipment, and money. The successful establishment and management of WtE plants may be facilitated by the formation of alliances between the private sector and the public sector.
4. Infrastructure Development
- Waste Management Infrastructure: Construction of sound integrated waste management mechanisms remain integral for WtE projects to take root in the regions. This includes formulation of waste to energy facilities, recycling stations and composting floors.
- Decentralized Waste Management: If decentralised systems of waste management are encouraged then feasible solutions can be provided to manage waste at a micro level. This can range from locations with small WtE plants that are located in urban or rural areas so as to minimize transportation costs and the adverse effect the plants may have on the environment.
5. Environmental and sanitary conditions
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Measures should be taken to ensure that no such damaging impacts are witnessed; possible risks on the environment need to be evaluated with lots of consideration before establishing WtE plants. This encompasses the assessment of the quality of air, water, and soil standard.
- Health and Safety Standards: Pursuing a proper health and safety regulation compliance is a must when it comes to WtE plants. This involves; implementing the controls that can be used to contain emissions, disposal of hazardous wastes and coming up with ways of protecting workers and the neighbouring groups close to the industries.
6. International Collaboration
- Learning from Global Best Practices: Learning from the experience of those countries, which have already implemented WtE projects, is possible. As it pertains to the county and competent jurisdiction this includes; regulating, technological advancement, and community engagement.
- Global Partnerships: One of the ways of viewing funding, technology and human resource is through entering into partnership with international organizations and experts. Focusing on WtE projects also involves the support of the Indian government and classification with other international counterparts can also act as a booster to WtE projects in India.
Eradicating the challenges encountered in implementation of waste to energy in India deserves a systemic and integrated endeavour. WtE holds much potential for India if India improves and gears up policies, deploys new-age technologies, involve public awareness and participation, build up infrastructures, and commit for environmental and health sustainability. There is no doubt India can work towards the change needed in waste management practices and create a cleaner and a greener environment.