The mission operated as part of Challenger 150 which UNESCO approved as a worldwide deep-sea research initiative. Scientists have obtained new insights into Antarctic drifting ice ecosystems through these research findings.

Scientists made an unexpected discovery of diverse life beneath Antarctica's frozen ice shelves. Scientists maintained their belief that extreme weather conditions and lack of nutrients would prevent life from surviving for several decades. The scientific world received a dramatic change in thinking because of this pivotal discovery. Science reveals that resilient sponge species and microbial organisms together with other life forms inhabit solid rock formations in an area that scientists once classified as uninhabitable because these species successfully endure harsh conditions. This surprising discovery reverses current knowledge about Earth's life limits and demonstrates new prospects for space-based life identification in comparable harsh cosmic environments. The survival of life in this deadly environment shows us important lessons about the power of adaptation. Underneath the ice surface researchers will find scientific responses which alter the common perception of survival strength in biological systems.
The Antarctic Ice Shelf
The Antarctic Ice Shelf stands among the most extraordinary and adverse natural structures that exist across our planet. Wide regions of the Southern Ocean showcase these ice extents which develop from glacier sheets moving off continental landmasses through the sea into floating condition. The ethereal yet crucial formation of Antarctic ice shelves supports the Antarctic ecosystem stability and moderates global sea levels.
The outstanding features which define ice shelves stem from their substantial sizes. The Ross Ice Shelf stands as one of the largest floating ice masses that stretch over hundreds of kilometres thus matching the territorial size of complete nations. Glacial ice encounters resistance from these natural barriers which reduces their speed during their migration process toward ocean waters. A contrasting aquatic world exists beneath the spotless frozen ice regions of Antarctica.
Scientists have discovered that Antarctic Ice Shelf historical regions exist in extraordinary geological conditions. Previous theories stated that such conditions of dark bleakness alongside freezing temperatures and scarce nutrients made survival impossible for living organisms. Recent research reveals that life exists in flourishing ecosystems which have managed to attach themselves to the ice's bases. This ground-breaking discovery transforms our knowledge about Earth's locations with extremely harsh conditions.
The scientific value of the Antarctic Ice Shelf produces effects which reach beyond pure scientific discovery. The Antarctic Ice Shelf maintains historical climate records within its frozen stratification through its geological record keeping abilities. The Antarctic Ice Shelf faces serious threats from climate change because its melting has become a critical worldwide issue which affects ocean levels and environmental equilibrium.
The Antarctic Ice Shelf acts as Earth's environmental watchdog leading scientists to study the vulnerability and capability of natural systems facing environmental changes. Scientists have yet to identify all the secrets that exist beneath the Antarctic ice which opens up unlimited opportunities for both research and discovery.
The recent Discovery
Recent science discovered organisms within Antarctic ice shelf making it a ground-breaking discovery across all fields of study. For many years scientists viewed this ice-covered world as a location that could never nurture living organisms because it lacked sunlight and extreme temperatures made it uninhabitable. The scientific expedition that aimed to pass hundreds of meters of solid ice unexpectedly uncovered an astounding discovery of active ecosystems with resilient life forms.
The team applied sophisticated drilling equipment and distant-operated vehicles to break through massive ice layers which exposed the under-laying rock terrain. What they found defied expectations. Different types of sponges together with filter feeders and organisms were observed living on the rocks despite permanent darkness and harsh cold conditions. The area devoid of sunlight presents harsh conditions which most living organisms need for survival while researchers believed the area lacked important sustenance. The organisms existed in apparent good health within this emotionally detached environment.
The scientific world reacted to these findings with combination of astonishment and enthusiasm. The initial scientific hypothesis indicates that these existing organisms perform chemosynthetic operations for energy generation instead of using sunlight similarly to organisms around deep sea hydrothermal vents. Remote locations where life exists indicate unknown survival and adaptive strategies are at work.
The scientific breakthrough reaches well beyond its territory in Antarctica. This discovery changes fundamental ideas about life-supporting environments while generating fresh interest regarding extra-terrestrial microorganisms. The study illuminates Earth's biological toughness because it demonstrates harsh environmental conditions can protect remarkable life sanctuaries.
Why Scientists Were Surprised?
The discovery of living organisms underneath Antarctic ice shelf surprised scientists because it disproved the widely accepted beliefs about survival conditions. Scientists considered this dark environment with frozen cold temperatures and negligible nutritional sources among the least habitable areas worldwide. Scientists established a belief during decades that such environmental conditions either supported no life or very minimal life. The find of living organisms shattered established scientific opinions about conditions needed to support life.
The main reason for astonishment stemmed from the lack of sunlight beneath the profound ice cover. Photosynthesis as a process which powers most Earth life requires sunlight to continue functioning. Scientific understanding indicated that the environment below the ice had no essential energy source to nurture ecosystem development. The distant discovery location from open waters with abundant nutrients made scientists question the survival energy sources used by these organisms.
These extraordinary adaptations came as a surprise to scientists who studied the discovery. Live organisms beneath the ice surface use chemosynthesis to generate energy because sunlight is unavailable to them. Such life forms demonstrated a strength and adaptability which researchers had failed to recognize. Research findings indicated that scientists lacked understanding regarding the mechanisms which transported nutrients because of ocean currents and melting glacial sediments.

The discovery totally changed society's understanding about Earth's life zones and opened new questions regarding Astrobiological investigations. Extremophile organisms living in remote icy areas of Earth demonstrate the potential for similar microbial life to exist in similar distant planetary regions such as Europa and Enceladus. Scientists encountered unexpected excitement toward unexplored regions after this discovery while trying to uncover deeper secrets about how life maintains itself.
Implications for Science
Science will face significant implications because researchers discovered living organisms underneath Antarctic ice which challenges current scientific models and establishes new research areas. The discovery of living organisms in a hostile environment implicates scientists to redefine the basic requirements which determine habitable zones from Earth to other celestial bodies.
The discovery shows remarkable significance regarding how life can adapt. Life that thrives in these extreme conditions shows resistance because it survives without light and uses chemosynthesis as an alternative energy source. Such research redefines what we understand about the ecological world since it demonstrates that life survives where it was previously considered uninhabitable. Research into survived organisms provides understanding of the evolutionary tools they use to stay alive during severe stress conditions.
The discovery has brought considerable interest to astrobiologists studying beyond Earth. Scientific evidence shows that dark, icy conditions lacking nutrients can support life in Antarctic ice shelf areas and potentially exist on comparable planetary bodies. Research into extra-terrestrial life becomes more promising because scientists now focus on icy moons such as Europa and Enceladus which contain subsurface oceans under layers of ice.
This discovery triggers research questions about the unexplored life-bearing areas of Earth. The investigation of under-glacial neighbourhoods remains scant while offering scientists the potential to discover new species along with their connection to worldwide biodiversity. The conservation of fragile ecosystems faces risks because they remain exposed to potential threats from climate change along with human encroachment.
The discovery underscores the necessity of developing cutting-edge scientific research technology. Scientific exploration of such distant challenging areas depends critically on robotic research systems together with precise drilling mechanisms. The technological progress helps us conduct comprehensive studies of extreme Earth regions while simultaneously developing capabilities for upcoming space explorations. Science keeps evolving due to human curiosity combined with unpredicted discoveries in Antarctica.
Challenges and Next Steps
Research at Antarctic ice shelf depths demands advanced logistical capabilities together with extensive scientific expertise from multiple nations to tackle both issues. This extreme location stands as the most distant earthly realm because it contains hundreds of meters of thick ice layers. Scientists operate sophisticated equipment to drill through Antarctic ice layers because contamination of the pure subsurface environment remains their foremost concern. Research becomes more complicated due to the challenge of preserving biological samples while they exist in freeze conditions.
The main obstacle for researchers stems from conditions in the hostile environment. Exploratory activities become challenging because sub-zero temperatures and complete darkness affect exploration while even advanced equipment faces failure in such extreme conditions. Remote missions present technical challenges primarily because rarely sufficient operational funds exist to secure fundamental tools needed to execute underwater research with systems such as ROVs and cutting-edge drilling equipment.
Scientists want to understand the specific adaptations and survival strategies of organisms that inhabit this ecosystem as a part of their research. The evaluation of ocean creatures' chemosynthesis-based nutrition and ocean current nutrient consumption requires state-of-the-art lab equipment. Researching interactions between organisms and their evolutionary development in the isolated environment poses one of the most challenging areas of scientific investigation.
Progress in Antarctic ice shelf life exploration will involve the creation of better methods for biological observation and sampling. Autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) equipped with high-resolution imaging systems will serve as essential non-invasive exploration tools because they reduce environmental disturbances during surveys. Scientists work to chart the seafloor territory beneath ice shelves when they study the systems that move nutrients across the ecosystem.
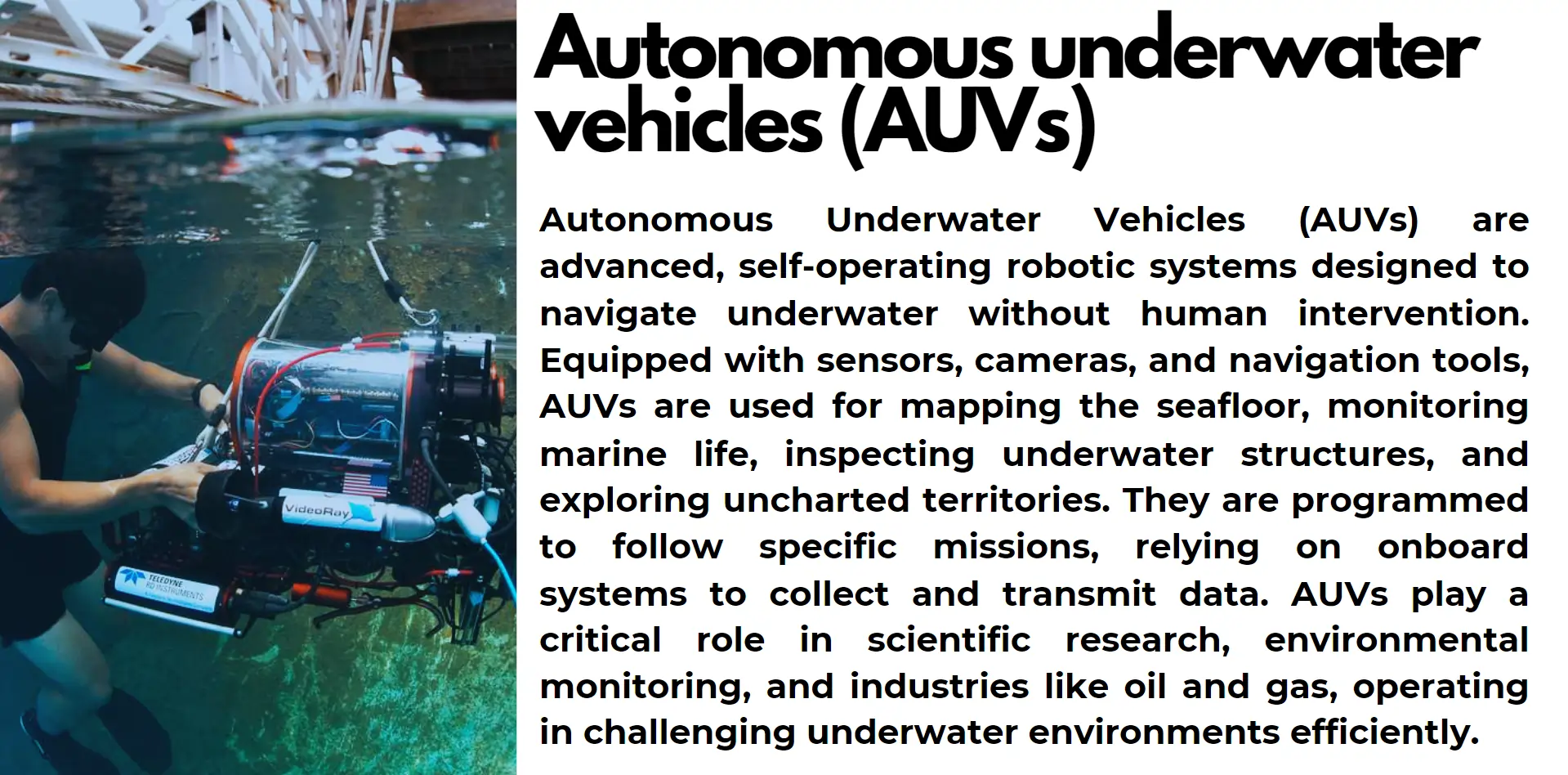
Methodical joint international cooperation will facilitate resource pooling and expertise exchange for achieving scientific goals while research teams need to follow environmental protection standards. Scientists now explore this previously unknown area because it enables them to understand the adaptability of life better while locating new discoveries that encourage future scientific advancements in this exciting field.
Broader Significance
This scientific breakthrough of Antarctic sub-glacial life extends great importance toward scientific expertise and broader human understanding. Life has proven its remarkable ability to survive across different environments thus breaking traditional beliefs about how organisms can find habitable territory. Scientists gain awareness through these findings about nature's ability to resist extreme adversity even in environments considered completely hostile.
The scientific discoveries enable new research opportunities for extreme ecosystem exploration which leads scientists to investigate previously hidden planetary regions. Scientific studies of Earth’s organisms deliver profound details about biodiversity as they demonstrate how various ecosystems function to support the planet’s equilibrium. Underneath the ice shelves scientists discovered life forms that could lead to discoveries of biochemical functions which will advance medical fields as well as biotechnology practices while supporting environmental research.
Exploration of outer space by humans receives extended relevance from this scientific discovery. The discovery of life in this tough environment on Earth allows scientists to develop greater abilities to assess whether similar ecological niches harbour life in space. New findings can better support for external life since scientists found they have subsurface oceans under their icy crust layers. Space science advances alongside this find which strengthens space exploration programs through international team work for off-world life investigation.
Future preservation depends heavily on preserving the global environment according to research evidence. The Antarctic ice shelves exist as sensitive ecological habitats that climate change threatens more significantly. Protection of these habitats remains essential because they support biodiversity conservation and worldwide regulatory functions.
Conclusion
Anthropic understanding of biological survival capacity underwent a significant change because of the Antarctic ice shelf new discovery. The scientific world now understands how organisms can survive after this discovery and scientists must begin planetary existence research while recognizing Earth's hidden ecological systems. Scientists made two essential discoveries from Antarctic ice life detection which establishes space life investigation possibilities and crucial awareness about protecting planet Earth ecosystems. People should grasp that living organisms maintain perpetual adaptability for innovative discoveries in mysterious zones.