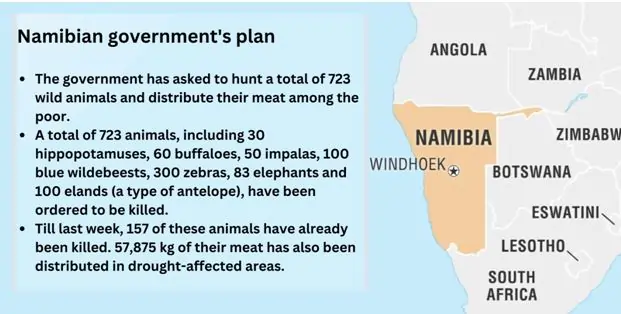
The Namibian government announced a controversial plan on 29 August
under which Namibia has ordered the killing of hundreds of its
wild animals to provide meat to 1.4 million people facing
hunger.According to the Namibian government, they believe
that to meet there food needs and to reduce the human-wildlife
conflict they need to go to tradition ways.
What is the cause of drought in Namibia?
- Namibia's geographical location is in a drought-prone area Due to which it often faces frequent droughts.
- The Draught that had happened in the Namibia is considered by several geologists as Devastating and it has a widespread over the region.
- According to data from the Namibia Meteorological Service, annual rainfall has decreased by 30 percent in the last decade.
- The situation has worsened mainly due to El Niño, with the El Niño phenomenon returning after seven years in 2023, causing above-average temperatures and minimal rainfall across the region.
- Namibia receives the most rainfall in February. But this year, not even 20% of the rain that was expected in this month fell. Almost of the Namibia is drought-prone. The situation has gone from bad to worse due to less rainfall.
- According to a report by the European Commission, the drought began in Botswana in October 2023, spread and intensified in Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe and Namibia, and is affecting much of southern Africa today.
What are the causes of hunger in Namibia?
- Prolonged drought has severely impacted water resources and agricultural production, worsening the desert country's food insecurity.
- A July 2023 report from the Ministry of Agriculture, Water and Land Reform shows that total cereal production for 2022-23 was 153,000 metric tons, down from 168,200 metric tons in the previous season.
- Between the months of July to September there is always a less availability of food in the region which ultimately lets to the worst conditions. Staple crops such as maize have dried up, killing large numbers of livestock.
- According to a UN spokesperson, on 23 August, about 84% of the country's food reserves have been exhausted. As reserves are low, prices have skyrocketed, restricting access to food for a large number of people.
The Namibian government's view on wildlife slaughter
- Wildlife slaughter is part of a broader strategy to address food shortages and reduce the risk of human-wildlife conflict.
- There is a struggle between the man and animal for the survival. By reducing their numbers we can reduce pressure on people and the environment.
- Wildlife slaughter aims to reduce the adverse effects of drought on wildlife conservation. According to the government, current grazing pressure and water availability can be managed by reducing the number of wildlife in national parks and protected areas where the number of wildlife exceeds the available resources.
Wildlife conservationists and nature lover's view against the killing of wildlife
- It will only cause disruption to the ecosystem and put already vulnerable species at risk.
- It is considered to have a major concerns regarding biodiversity.
- Loss of wildlife affects tourism, which is an important sector for Namibia's economy.
- The order to kill the animals is also being linked to politics as Namibia is due to have presidential elections in November.
- This will also encourage other governments in Africa to exploit wildlife under the guise of humanitarian relief.
- Elephants are important for the ecosystem and their destruction will be disastrous.
- With regard to killing and eating wildlife, experts have warned that such measures may inadvertently promote the spread of highly infectious zoonotic diseases.
What is Drought?
According to the American Meteorological Society Drought for instance is described as “a condition characterized by a lack of adequate moisture over a period of time ranging from a season to several years that lead to water shortage”.

Types of Drought
In order to understand drought and to be able to observe it experimentally scientists have subdivided it into the following types:
- Meteorological Drought: This is so especially when a region experiences dry weather conditions. In other words, it is a absence of rains.
- Hydrological Drought: Hydrological drought occurs when it becomes rather easy to discern that the supply of water is low in rivers, lakes as well as reservoirs. It ultimately alters the water system causing its low availability.
- Agricultural Drought: One has a picture of dry and arid fields and shriveled crops. Agricultural drought takes place when agricultural crops are affected by the water shortage.
- Socioeconomic Drought: It is when these different flows (for example, of food, energy or even water) are affected by the shortage of water due to drought. Thus, it is not only about water and dry plants, but it also affects the world’s economies and people’s earnings.
- Ecological Drought: It impacts on the community and Mother Nature as well. Ecological or hydrologic drought is a result of a change in ecology or the condition of natural ecosystems including forests, wet lands and wildlife habitats.
Impact on Eco-system:
- Plant Growth loss: Plants are no exception in this case and depending on the availability of water, plants will be affected. They include grasses, shrubs, and even very big trees, and they are greatly impacted on in regard to their growth by less soil moisture. Leaves of plants become dry and shriveled; petals fall off flowers while seeds have a hard time germinating. Think of a green jungle that seems to have waned in colors gradually into an arid environment.
- Increased Fire and Insect Outbreaks:
- Wildfires thrive in environments which are created by drought. Dry vegetation turns into a combustible material and all that is needed is a source of fire to burn large pieces of land. These fires negatively affect ecosystems by eradicating the habitats, emitting carbon stored in the forests and changing the physical properties of the soil.
- Insects too favor it; may be due to scarcity of water they can easily survive. For instance, bark beetles prefer the trees that have been already under stress and thus cause massive death in forests.
- Altered Rates of Carbon, Nutrient, and Water Cycling: It is also very important to view ecosystems as cycles of life. Drought disrupts these cycles. For instance:
- Carbon cycling slows down: Plants decrease their ability to use CO2 through photosynthesis and this impacts the global carbon budget.
- Nutrient cycling falters: It occurs where the water content of the soil is low due to a problem with its aeration, something that hinders the function of soil microbes that are considered as beneficial to plants to provide nutrient.
- Water cycling shifts: Rivers are formed by streams thus when the streams dry up the aquatic life is affected badly and in addition the amount of water re charged in the ground is reduced.
It is as if one day the ecosystem has lost the beat; nutrients clash with roots, water molecules don’t know where to go.
- Local Species Extinctions: SEVERE Drought Compels Some Species to the Verge of Extinction. if that habitat loses its moisture, then the amphibian stands a good chance of becoming extinct.Even common species suffer. Birds, mammals and insects are the species that bear the consequences of habitat loss in the form of food and nesting areas. The delicate balance shifts and some of the players are ejected for eternity.
- Human-Ecosystem Interplay: Nature can be changed through conversion for development, utilization of water resources and pollutions.At present, water in the wetland is being utilized for its function while water is also taken from it to meet human activities.Well, if you do not take ecosystem water requirements into consideration while making the allocations disaster happens. These dry up, and the benefits that wetland provides such as filtering of water and averting soil erosion disappears.
Measures towards overcoming Drought Disaster amongst African Countries
1. The Great Green Wall Initiative:
Recovery of Life and General Well-being
- What is it? Great Green Wall Initiative (GGWI) is a project that covers 8000 Km across the continent from Senegal to Djibouti. It is an afforestation program which is designed and implemented to arrest land degradation which is the main reason for desertification.
- How does it work? More than twenty countries take part in the project, which aims at afforestation for purposes of soil replenishment. In other words, the GGWI enhances the food security, creates income and locks carbon. This green belt is supported by FAO, IFAD and Green Climate Fund to develop employment opportunities and mitigation of drought problem.
- Goals: The GGWI’s overall goal is that by 2030, it will have restored 100 million hectares of land, amassed 250 million tons of carbon and generated 10 million jobs. Drought is perhaps one of the deadliest effects of climate change thus this is a positive step towards addressing the issue of drought.
2. Reusing Rainwater:
It is proposed to examine Tunisian practices, which will be referred to as a Tunisian Approach.
- Context: In this country, water resources during specific periods of the year are scarce, and the above resources cut down by up to 40%.
- Solution: Rainwater harvesting! Things like, and this is very typical of the tropics, storage of rain water in tanks during rainy season and using the same during dry season. Rainwater harvesting is done in several ways such as rooftop catchment systems, and also the community reservoirs.
- Impact: It means that water supply in agriculture, households and for livestock is more reliable and can be relied on most of the times.
3. Improving Groundwater Recharge
- Beneath the Surface: Within this context, it can be stated that for Africa, groundwater can be considered as its best kept secret. The vegetation is also useful during the times of the drought because it recharges the aquifers during the wet season.
- Methods: Rain harvesting provides potential recharge zones to enable water to infiltrate and recharge aquifers by means of managed aquifer recharge, artificial recharge basins and natural infiltration zones.
- Benefits: Including water quantity and quality for public use of water, for irrigation and for sustainable environments.
4. Preserving Humidity in Fields
- Smart Farming: Today, the African farmers have embraced the act of conservancy. The use of cover crops, reduction of tillage and practices in agro-ecology help in retention of moisture on the soil.
- Mulching: For example, people can use straw, leaves or other crop residues around plants to prevent water evaporation and soil heat.
- Result: Stable production yields in the periods of continuously favorable weather for the crops.