
Following the Second World War, the collaboration among the Soviet Union, the United States, and Britain ceased, leading to the re-emergence of longstanding tensions. Relations between the West and Soviet Russia rapidly declined, notwithstanding the absence of an actual conflict between the two opposed blocs. Cold war is believed to be started after the end of the Second World War. Notwithstanding numerous amicable connections, the Cold War persisted until the dissolution of communism in Eastern Europe (1989-91). Reciprocal animosity compelled the rival countries to engage in competition over propaganda and economic issues, necessitating adherence to a broad policy of non-cooperation.
The two superpowers, the US and the Soviet Union, brought in friends around them. From 1945 to 1948, the Soviet Union instituted communist regimes in the majority of Eastern European nations, including Poland, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, Yugoslavia, Albania, Czechoslovakia, and East Germany (1949). In 1948, a communist government was founded in North Korea and the communist group gained more dominant after Mao established a communist government in China.
Conversely, America fostered a friendship with Japan and commenced aiding its rapid reconstruction. America provided substantial financial assistance to Britain and 14 other European nations, including Turkey, which facilitated the formation of an anti-communist coalition. The second group construed the activities of one group in an atypical manner. A long battle of words continued, for example, the border dispute between Poland and Germany, no lasting treaty could be made respecting Germany and Austria. Following Stalin's demise in 1953, the new Russian leadership initiated discussions on peaceful coexistence, leading to a thaw in hostilities and the emergence of amicable relations. In 1955, an agreement was made to withdraw the army from Austria but no agreement could be reached on Germany. Tensions rose over Vietnam and Cuban missile crisis.
Reason for Cold War
a) Difference in ideals: The main basis for the Cold War was the theoretical disagreements between the communist and capitalist state or liberal-democratic state. The communist system was based on Karl Marx's theories. He believed that the nation's property should be in common ownership and everyone should have some ownership in it. The economy should be centrally planned and the workers' benefits and better life should be protected by the state's social policies. In the capitalist system, they believed private ownership. Capitalism is controlled by profit-based private entrepreneurship and the power of private property is safeguarded in it.
b) Stalin's foreign policy worsened the tension: His purpose was to strengthen Russian dominance in Europe through military power. After the defeat of the Nazi army, he strove to conquer as many German lands as possible; the same effort was made with Finland, Poland and Romania. He also obtained success in this but the western countries grew vigilant against Russian aggression, they believed that Stalin wanted to promote communism more and more in the world.
c) American and British politicians were antagonistic towards the Soviet regime: Roosevelt was cordial towards Russia during the war and also assisted it under the Lend-Lease system but Truman, who became the President after Roosevelt's death in April 1945, suspected the communists. Some historians consider his dropping of the atom bomb on Japan as a threat to Russia. Stalin always looked at Britain and America with distrust for ending communism. The delay in striking the second front, France, intensified German pressure on the Russians. The Western countries notified Stalin about the atom bomb just before unleashing it on Japan. He rejected the Russian takeover of Japan. Above all, the West had the atom bomb and the Soviet Union did not.
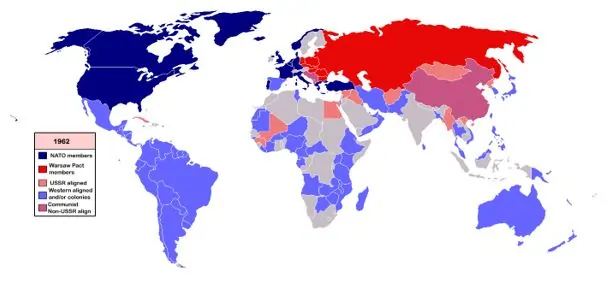
Various dimensions of the Cold War
1. Establishment of Communist administrations throughout Eastern Europe
At Yalta, the United States, Britain and the Soviet Union had decided that the three nations would aid the liberated Europe to develop democratic institutions through free elections. Initially, coalition governments were founded in the countries freed by the Soviet Union, which included the Communists. But within three years, other parties were ejected from the governments of all these countries and the Communists secured complete power over them.
Poland: In 1946, the temporary government of Poland, which also included the leaders of the anti-Soviet émigré Polish government located in London, divided. In the elections that were held later, the Communist Party, which was a coalition of several parties named the Polish United Labour Party, obtained 90 percent of the seats. The leaders of the main opposition party argued that the elections were not held openly.

Czechoslovakia: The coalition government that was founded in 1946 included leaders of the Communists and other parties. In February 1948, the communists urged that the government should be rebuilt since some of the parties in the cabinet were sheltering the fascists. When the restructuring was done, it was reported that Czech President Eduard Benes did it under pressure from Russia. As a result of the restructuring, a government dominated by communists came to power.
Similar incidents took place in Bulgaria, Romania, Hungary. In Yugoslavia and Albania too, communists who had led the national resistance had come to power. Thus, following Russia, communist regimes had been created in seven countries of Europe. Britain and the United States regarded this development a threat to independent states.
Germany: After the Second World War, Germany was divided into four occupation zones, each of which was held under the occupation of the Soviet Union, the United States, Britain and France. Gradually, Germany was divided into two sections, one portion of which stayed under the occupation of the western capitalist countries and the other under the socialist structure of Soviet Russia. The western section stopped supplying industrial machinery to the eastern parts, while the eastern part stopped giving agricultural produce to the western part. Thus, the economic unity of Germany was dissolved. In the eastern half, the land was handed from the landlords to the peasants and the industries and mines were nationalized. In the western region, a capitalist form of economy started developing which was assisted by America.
Greek Civil War: The communists played a big role in the resistance to the fascists in Greece but the British troops dispatched to Greece planned to re-establish the king there, this was considered as a major reason behind the civil war outbreak. But at the beginning of 1947, Britain chose to call back its forces from Greece, after which America decided to aid the Greek government. Along with this, Turkey also started getting American support in view of the communist menace. This escalated the friction between Russia and America.
Formation of NATO: In April 1949, the United States, most of the countries of Western Europe - Britain, France, Belgium, Luxembourg, Holland, Norway, Denmark, Portugal and Italy, Iceland and Canada created an alliance named the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Through this partnership, they initiated a comprehensive weaponry program to curb Russian expansionism and communism in Europe.
Two states in Germany: In May 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) was created with Bonn as its capital. It was made a member of NATO in 1955, before that Greece and Turkey were made members of NATO in 1952. Sometime after the formation of West Germany, the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) was created. This split of Germany lasted for more than 40 years. Finally, this division ended with the union of both on 3 October 1990.
Warsaw Pact: The Soviet Union and the countries of Eastern Europe dominated by the Communist parties formed a military alliance known as the Warsaw Pact Organization. Like NATO, it too had its own unified military command. Meanwhile, in other regions of the world, additional treaty organizations such as SEATO, CENTO etc. were founded under the guidance of America.
Rise of Soviet Union as a Nuclear Power: With the nuclear test by the Soviet Union in 1949, the four-year-long monopoly of the United States on this weapon ended. Since then, the creation of greater and more lethal weapons developed as a horrible consequence of the Cold War. These weapons further intensified international tensions and conflicts.
Korean War: 1950, 38 degrees dividing line between North Korea and South Korea. In August 1948, under American influence, South Korea announced itself as the Republic of Korea, whereas in September 1948, under Soviet influence, North Korea declared itself as the People's Republic. The Soviet Army and the American Army withdrew their soldiers from Korea by 1949. The leader of North Korea was Kim Ul Sung and that of South Korea was Syngman Rhee. Both the administrations opposed division and made unification their objective, as a result of which a conflict broke out between the two in June 1950. The United Security Council considered North Korea responsible for this war and agreed to support South Korea, under which America landed its force in South Korea. The occupation of Seoul by North Korea was finished and it was pushed back from South Korea. At the same time, China sent its force into this battle on support of North Korea, thanks to which the American army had to retreat. WAR ended in 1953. There were many ceasefire talks and was a major contributor to it. As a result, the situation before the conflict was restored. In this war, around 1.5 lakh Americans and 30-40 lakh Koreans were slain. After the world war-I US came up with such big participation for the first time. Despite this, it was a local war. However, the possibility of it becoming global remained constant. The US commanding general planned to strike China and there was also a possibility of the use of nuclear weapons.
Vietnam War: Due to the restriction policy of communism, the United States had to get involved in a long war in Vietnam. Vietnamese Republic was founded by nationalists. Ho Chi Minh was the leader. After the Second World War, the French tried to re-establish their power there. Britain and eventually the United States aided them in this job. The Vietnamese army under the command of Ho Chi Minh received support from the Soviet Union and China. In 1954, the French army had to face a catastrophic setback. At Dien Bien Phu French got a major set back. On this occasion, the American President rejected Dulles' proposal to send American soldiers to Vietnam. According to the Geneva Agreement in 1954, French authority over Vietnam ended. As a temporary solution Vietnam was divided into north and south. After the elections of 1956 Vietnam was to be made one by joining both parts.
Missile crisis in Cuba: In 1959, a revolution took place in Cuba, 150 miles from the southern tip of the United States, under the leadership of Fidel Castro. When the new administration started taking dramatic social and economic moves, initiated land reforms and started nationalizing companies, the United States established a hostile approach against it. Another reason for this was that the new government had started forging friendly relations with Russia. In April 1961, the US landed 2000 Cuban exiles on the coast of the Bay of Pigs with the purpose of overthrowing the Cuban government but the attack was thwarted. Then the then US President Kennedy warned that we are not ready to leave Cuba in the hands of the communists. In October 1962, the United States came to know via its spy planes that the Soviet Union was developing missile bases in Cuba. This was deemed a severe threat to the security of the United States. On 22 October 1962, Kennedy imposed a naval and air blockade of Cuba which meant that the United States would stop any plane and ship moving towards Cuba. He also intended to attack the missile bases of Cuba. But this crisis that could have led the world to the edge of annihilation was averted when on 26 October Soviet President Khrushchev conveyed a message to Kennedy that if the United States promised not to invade Cuba, the Soviet Union would remove its missiles from there. The United States also agreed to relocate its missiles stationed in Turkey near the Soviet Union.
Arab-Israeli War: In 1967, Egypt, Jordan and Syria waged a 6-day war with Israel. The Arab governments were defeated and Israel conquered Egyptian territory in the Sinai Peninsula, the western bank of the Jordan River, Jordanian territory and the Gaza Strip, and a part of Syrian land called the Golan Heights. Israel established sovereignty of the entire city of Jerusalem. A third Arab-Israeli war took occur in 1973. During this war, the oil-producing Arab governments declared that they would stop delivering oil to any country that was helping Israel. This led to the European countries of NATO declining to back Israel, prompting the United States to encourage Israel to agree to a truce. Israel has refused to leave the Arab regions it seized in the wars of 1956, 1967 and 1973. But discussions between Israel, Arab states and the Palestinians in recent months appear to have opened the way to the possibility of peace in the area.
The END of COLD WAR
The Cold War which was that political and ideological rivalry between the United States and Soviet Union was a long-drawn one the periodical impact of which was felt in reshaping the world politics. Here are some of reasons due to which it came to an end:
Communist Bloc Unravelling: During the nineteen fifties through the seventies there were signs of weakness in the originally closely-knit fellowships of the communists. China and the Soviet Union split and the lesser countries began to rebel against super powers. Economic independence made situations in Japan and the West more tense and made international relations even more complicated.
Gorbachev’s Reforms: Mikhail Gorbachev Russian leader recognised the necessity for the transformation. He went ahead and eliminated totalitarianism in the Soviet government and advocated for political democracy. He dismantled communism, emasculated the communist party as an authority across the Soviet bloc and decentralised power to the affiliated governments.
Eastern Europe’s Transformation: Communist states in Eastern Europe started to break down. Democratic governments were installed in East Germany, Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia. Ideally, symbolic of the end of division is the event that took place in Berlin in the year 1989 known as the Berlin Wall. On the 3rd of October West and East Germany united under NATO protection.
Soviet Union’s Collapse: The worst happened in late 1991, The Soviet Union split up into fifteen entirely new nations. Russia itself has come out with an anti-Communist leader. The division by the ‘Iron Curtain’ was done away with and thus brought about the official end of the Cold War.