The Chhattisgarh Public Service Commission (CG PSC) is one of the very reputed organizations of Chhattisgarh which is involved in organizing numerous examinations in the state. Many students sit for the CG PSC exams and it is vital that those in their early stages of preparation understand the important points about them including the eligibility and syllabus to have a well-developed plan. They also include the age limits, education standards, and even the nationalities of the candidates to apply for the job so as to screen the candidates in order to keep only the most appropriate. It is very important to clearly understand what the syllabi for the Preliminary and Main examinations include, since the examination board is very vast, covering a number of subjects and topics. The Preliminary exam also does not contain the questions related to the specific subjects, rather it is a screening exam that tests the candidate’s basic IQ and General awareness while the Main exam is a much tougher examination that is designed to test the candidate’s knowledge on the particular subjects and his ability to apply his mind and analyse the problems. The candidates that are preparing for CG PSC, a clear overview of the eligibility and syllabus is mentioned below:
Eligibility
- Nationality
- Qualification
- Age
- Number of Attempts
Let’s deal with each aspect one by one-
Nationality
- Aspirants appearing for the Chhattisgarh PSCexamination must be Indian citizens.
Education Qualification
This exam has a certain requirements out of these one is the Educational Qualification which form the important part of eligibility for the examination:
- There is a provision to appear in the examination only for candidates who have done their bachelor degree from a recognized board or institution under Central and State Government
Age
The requirements stipulated and demanded by the Chhattisgarh Public Service Commission (CG PSC) for the people that wish to sit for the Chhattisgarh state civil service examination involves age requirement. For age related quarries Aspirants may look below:
- The application for the test can be made from an individual who is 21 years of age and not above 30 years.
- For those who are Domicile to Chhattisgarh has an Upper Age limit of 35 years.
Age relaxation is also extended to the different category students as per the norms prescribed by the state government of Chhattisgarh.
| Scenario |
Age Relaxation in years |
| Candidates who are native of Chhattisgarh and has an upper age limit of 35 years |
5 years of respite at age 35 not more than five years |
| Those candidates who are appointed on a contract basis |
The candidate's age should be a maximum of 38 years |
| Those candidates who are either domicile or bonafide ST, SC, Women disabled, OBC according to the given record by the Government of Chhattisgarh |
The age limit for those candidates should be 45 years |
| Those candidates who are applying for the post is a window on the first appointment |
Candidates like these get an age relaxation of up to max 5 years |
| Those candidates who have green cards with them under the programme named Family Welfare programme |
Such candidates get age relaxation up to a maximum of 2 years |
| Those aspirants who are working either as permanent or temporary employees of Chhattisgarh or the State Government |
These aspirants get an age relaxation of 38 years |
| Candidates who have been involved in Military service for a minimum of 5 years |
These candidates get age relaxation up to a maximum of 5 years |
| Candidates with disabilities |
Such candidates get an age relaxation of 5 years |
| Candidates who are government servants and are retrenched |
These candidates have an age relaxation of 3 years |
| If a potential candidate is of Indian descent and moved from Sri Lanka, Burma and East Pakistan |
These candidates get an age relaxation of a maximum of 3 years |
| If the applicant is the winning couple from the inter-caste marriage programme supported by the tribal Harijan and backward class welfare department, in accordance with the GAD memo, |
Such candidates get an age relaxation of maximum of 5 years |
| Those candidates who are a sportsperson and are awarded the Shaheed Rajiv Pandey award or Gunda Dhur, or a candidate recognised by Maharaja, Praveen Chandra Banda age Samaan or Rashtriya Yuva awarded as per GAD memo |
Such candidates get an age relaxation of a maximum of 5 years |
Number of attempts
Chhattisgarh PSC has not mentioned about the limit on the number of attempts for the Aspirants to appear in the examination.
Physical Standards
Candidates are expected to satisfy certain minimal physical criteria while applying for the CG PSC. CG PSC has prescribed different standards for Different posts as mentioned below:
Male Candidates
| Post's Name |
Height |
Chest Without Expansion |
Chest With Expansion |
| District Excise Officer |
163 cm |
79 cm |
84 cm |
| District Fighter |
165 cm |
84 cm |
89 cm |
| Excise Sub-Inspector |
165 cm |
81 cm |
85 cm |
| Dy. Superintendent of Police |
168 cm |
84 cm |
89 cm |
| Superintendent District Jail |
168 cm |
84 cm |
89 cm |
| Assistant Jail Superintendent |
165 cm |
80 cm |
-- |
Female Candidates
| Post's Name |
Height |
Min. Difference |
| District Excise Officer |
152.4 cm |
5 cm |
| District Fighter |
-- |
5 cm |
| Excise Sub-Inspector |
152.4 cm |
5 cm |
| Dy. Superintendent of Police |
155 cm |
5 cm |
| Superintendent District Jail |
155 cm |
5 cm |
| Assistant Jail Superintendent |
155 cm |
5 cm |
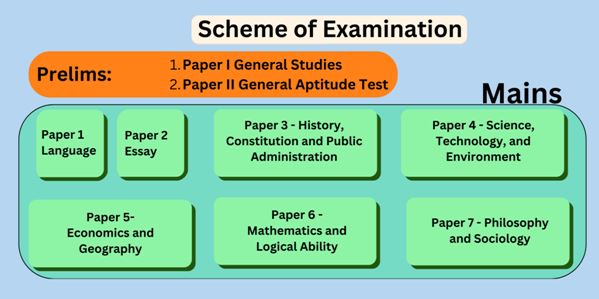
Chhattisgarh PSC Syllabus(Pre & Mains)
CGPSC Prelims Syllabus 2025 for Paper I
Part A: General Studies
- Indian Philosophy, Art, Literature and Culture
- Modern Indian history and the Indian National Movement.
- Indian Economy
- Physical, Social and Economic Geography of India
- Indian Constitution and Polity
- Environment and Ecology
- Current Affairs and Sports
Part B: General Knowledge of Chhattisgarh
- Administrative Structure, Local Government, and Panchayati-raj of Chhattisgarh
- History of Chhattisgarh and Contribution of Chhattisgarh to the Freedom Movement
- Tribes, Special Traditions, Teej, and Festivals of Chhattisgarh
- Geography, Climate, Physical status, Census, Archaeological and Tourist Centres of Chhattisgarh
- Economy, Forest, and Agriculture of Chhattisgarh
- Literature, Music, Dance, Art and Culture, Idioms and Proverbs, Puzzle/riddle, Singing of Chhattisgarh
- Current Affairs of Chhattisgarh
- Industry in Chhattisgarh, Energy, Water and Mineral Resources of Chhattisgarh
General Studies Paper II
- General mental ability
- Logical Reasoning
- Interpersonal Skills and Communication Skills
- Decision Making
- Knowledge of Chhattisgarh Language
- Data Interpretation
- Knowledge of Hindi Language
Mains
QUESTION PAPER-01 Language
भाग-1 सामान्य हिन्दी :-
भाषा-बोध, संक्षिप्त लेखन, पर्यायवाची एवं विलोम शब्द, समोच्चरित शब्दों के अर्थ भेद, वाक्याशं के लिए एक सार्थक शब्द, संधि एवं संधि विच्छेद, सामासिक पदरचना एवं समास-विग्रह, तत्सम एवं तद्भव शब्द, शब्द शुद्धि, वाक्य शुद्धि, उपसर्ग एवं प्रत्यय, मुहावरें एवं लोकोक्ति (अर्थ एवं प्रयोग), पत्र लेखन। हिन्दी साहित्य के इतिहास में काल विभाजन एवं नामकरण, छत्तीसगढ़ के साहित्यकार एवं उनकी रचनाएं। अपठित गद्यांश, शब्द युग्म, प्रारूप लेखन, विज्ञापन, प्रपत्र, परिपत्र, पृष्ठांकन, अधिसूचना, टिप्पणी लेखन, शासकीय, अर्धशासकीय पत्र, प्रतिवेदन, पत्रकारिता, अनुवाद (हिन्दी से अंग्रेजी तथा अंग्रेजी से हिन्दी)
भाग-2 General English:-
Comprehension, Precis Writing, Re arrangement and Correction of Sentences, Synonyms, Antonyms. Filling the Blanks, Correction of Spellings, Vocabulary and usage, Idioms and Phrases, Tenses, Prepositions. Active Voice and Passive voice, Parts of Speech,
भाग-3 छत्तीसगढ़ी भाषा :-
छत्तीसगढ़ी भाषा का ज्ञान, छत्तीसगढ़ी भाषा का विकास एवं इतिहास, छत्तीसगढ़ी भाषा का साहित्य एवं प्रमुख साहित्यकार, छत्तीसगढ़ी का व्याकरण, शब्द साधन संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, विशेषण, क्रिया, वाच्य, अव्यय (क्रिया विशेषण, संबंध बोधक, विस्मयादि बोधक) कारक, काल, लिंग, वचन, शब्द रचना की विधियों, उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय संधि (अ) हिन्दी में संधि, (ब) छत्तीसगढ़ी में संधि, समास, छत्तीसगढ़ राजभाषा आयोग,
छत्तीसगढ़ी भाषा के विकास में समाचार पत्रों, पत्रिकाओं, आकाशवाणी व सिनेमा की भूमिका, लोकव्यवहार में छत्तीसगढ़ी, छत्तीसगढ़ी भाषा का सामान्य परिचय-नामकरण, छत्तीसगढ़ी भाषा का परिचय, छत्तीसगढ़ी में क्रियाओं में वर्तमान, भूत तथा पूर्ण अपूर्ण वर्तमान भविष्य काल के रूप, काल, लिखना-क्रिया के भूतकाल के रूप, पूर्ण अपूर्ण भूतकाल, पढ़ना-क्रिया के भविष्यकाल के रूप, पूर्ण अपूर्ण भविष्यकाल, पाद- टिप्पणी।
QUESTION PAPER-02 Essay
PART-01: INTERNATIONAL AND NATIONAL LEVEL ISSUES
Candidates will have to write two essays on issues (Reason, present status including data and solution) from this part. Four problems will be given in this part; Candidate will have to write two essays on this part about 750-750 words. Each issue in this part will carry 50 marks.
PART-02: CHHATTISGARH STATE LEVEL ISSUES
Candidates will have to write two essays on issues (Reason, present status including data and solution) from this part. Four problems will be given in this part; Candidate will have to write two essays on this part about 750-750 words. Each issue in this part will carry 50 marks.
QUESTION PAPER-03
General Studies-1
PART-01 History of India:-
Pre-historic Age, Indus Civilization, Vedic Civilization, Jainism and Buddhism, Rise of Magadh Empire, Mauryan Polity and Economy, Sunga, Satavahana period, Gupta Empire, Development of Art, Architecture, Literature & Science during the Gupta-Vakataka Period. Major dynasties of south india, Medieval Indian History, Sultanate and mughal period,, Vijaya Nagar Kingdom, Bhakti Movement, Sufism, Development of literature in regional languages, Rise of Marathas, Advent of Europeans and factors responsible for the establishment of British Supremacy. Expansion of British Empire Wars and diplomacy, Rural Economy-Agriculture, Land Revenue Systems Permanent Settlement, Ryotwari, Mahalwari, Decline of handicrafts industries, Relation of East India Company with States. Changes in Administrative Structure, Urban Economy after 1858, Development of Railways, Industrialization, Constitutional Development.Socio- Religious Reform Movements Brahmo Samaj, Arya Samaj, Prarthna Samaj, Ram Krishna Mission, Rise of Nationalism, The Revolt of 1857, Establishment of Indian National Congress, Partition of Bengal and Swadeshi Movement, Rise and Development of Communalism, Revolutionary Movements, Home Rule Movement, Gandhian Movements. Quit India Movement, Workers, Peasant and Tribal Movements, reform movement among Dalits, reform movement among Muslisms, Aligarh Movement, Indian National Army, Independence and Partition of India, Merger of States,
PART-02 Constitution & Public Administration:-
Constitutional Development of India (1773-1950). Formation of the Constitution and Salient Features, Preamble, Nature of the Constitution. Fundamental Rights and Duties. Directive Principles of State Policy. Union Executive, Legislative and Judiciary. Right to Constitutional Remedies, Public Interest Litigation, Judicial Activism, Judicial Review, Attorney General. State Executive, Legislature and Judiciary, Advocate General, Centre-State Relationship- Legislative, Executive and Financial. All India Services. Union and State Public Service Commission. Emergency Provisions, Constitutional Amendments. Concept of Basic Structure. Govt. of Chhattisgarh Legislative, Executive and Judiciary. Public Administration- meaning. Scope, Nature and importance. Public Administration and Private Administration under Liberalizations. New Public Administration, Development Administration and Comparative Administration, New dimensions in Public Administration. State vs. Market. Rule of Law. Organisation- Principles, approaches and structure. Management Leadership, Policy determination, Decision making. Instruments of Administrative Management Co-ordination, Delegation, Communication. Observation and Motivation. Administrative Reforms. Good Governance, E- Governance. Bureaucracy. District Administration. Control on Administration in India Parliamentary, Financial Judicial and Executive. Lokpal and Lok Ayukta. Right to Information. Panchayats and Municipalities. Parliamentary Presidential, Unitary-Federal Government. Theory of Separation of Powers. Administrative Structure of Chhattisgrah.
PART-03 History of Chhattisgarh:-
Pre-historic Age, History of Chhattisgarh from Vedic age to Gupta Period, Major dynasties- Rajarshitulya Kula, Nala, Sharabhpuriyas, Pandu, Somvanshís etc. Kalchuris and their Administration, Chhattisgarh under the Marathas, British, Chhattisgarh under British protectorate. Former states and Zamindaris of Chhattisgarh, Feudatory States. Revolt of 1857, Freedom Movement in Chhattisgarh, Workers, Peasant and Tribal Movements. Formation of Chhattisgarh State.
QUESTION PAPER-04
General Studies - II
PART-01 General Science:-
CHEMISTRY: Rate of chemical reaction and chemical equilibruim Preliminary knowledge of rate of chemical reaction. Fast and slow chemical reactions. Metals Position of metals in the periodic table and general properties. Metal, mineral ore. Difference between mineral and ore. Metallurgy- concentration, roasting, smelting, refining of ores. Metallurgy of copper and Iron. corrosion of metals. Alloys. Nonmetals Position of nonmetals in the periodic table and general Properties. Some important organic compounds, some general artifical polymers, polythene, polyvinyl choloride. Teflon soap and detergents.
PHYSICS:- Light - nature of light, reflection of light, law of reflection, reflection from plane and curved surface, image formation by plane, convex and concave mirror, relation between focal length and radius of curvature, electric discharge in gases, causes of origin of energy in the Sun, Electricity and its effects electric intensity, potential- potential difference, electric curent Ohm's law. Resistance, specfic resistance, influencing factors, combination of resistance and related numerical questions, thermal effect of current and it's uses, calculation of power and electrical energy spent. (numerical) precautions observed in electric experiments, Photo electric effect, Solar Cell, Structure, PN Junction, Diode,
BIOLOGY: Transport: transport of mineral and water in plants and animals [in context of human being], structure and function of blood, structure and working of heart, [preliminary knowledge], Photosynthesis- Defination, main steps of the process. light reaction and dark reaction, Respiration Definition, breathing and respiration, Types of respiration, Aerobic and anaerobic respiration, respiratory organs of animals respiratory system of human being and mechanism of respiration, Human digestive system and digestive process [General infromation], Control and coordination Nervous system of human being. Structure and function of human Brain and spinal cord, coordination in plants and animal Phytoharmones, endocrine glands harmone and their function. Reproduction and growth type of reproduction Asexual reproduction, fission, budding, regeneration, artificial vegetative reproduction, layering, cutting, grafting, Porthenogenesis, sexual reproduction in plants, structure of flower and reproduction process, [general information] pollination, fertilization. Human reproductive system and reproduction process. [general information], Heredity and evolution heredity and variation. Fundamental basis of heredity chromosome and DNA [preliminary information]
PART-02 Aptitude Test, Logical Reasoning, Mental Ability :-
Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of rational numbers. Finding the rational number between two rational numbers. Ratio and Proportion definition, properties, aternendo, invertendo, componendo etc. and their uses. Commercial Mathematics Banking, calculation of interest on/in savings account, fixed deposit account and recurring deposit account. Calculation of income tax (for salaried person and excluding house rent allowance). Factorization, LCM, HCF. Vedic Mathematis addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and checking the answer through bijank. Square, square roots, cube, cube roots, vinculam and its application. The application of vedic mathematics methods in algebra etc.. Introduction and creativity of Indian Mathematician in reference with Aryabhata, Varaha mihira, Brahma gupta, Bhaskaracharya, Shrinivas Ramanujan. Mathematical operations, Basic numeracy (numbers and their relations, order of magnitudes etc.). Data interpretation (charts, graphs, tables, data sufficiency etc.) and analysis of data. Arithmetic mean, Median, Mode, Probability. Question related to addition and multiplication theorem on probability. Applied mathematics Profit and Loss, Percentage, Interest and Averages. Time, speed, distance, river and boat. Analog Test, Odd word, Odd pair of words, Coding & Decoding Test, Relation Test, Alphabet Test, Mathematical Operations, Logical analysis of words, Inserting the missing number or word, Assertion and Reason, Situation reaction test, Figure series, Deletion of elements, General Mental ability.
PART-03 Applied & Behavioural Science:-
Role of Information Technology in Rural India, basic knowledge of computer, computers in communication and broadcasting, software development for economic growth. Broad applications of IT. Energy Resources: Demand of Energy, renewable and nonrenewable energy resources of energy, the development and utilization of nuclear energy in the country. Science & Technology developments in India in present, origin of agriculture. Progress of Agricultural Science and its impact, Crop science in India, Fertilizer, Control of pests and disease scenario in India. Bio-diversity and its conservation General introduction defination, species and genetic diversity, Bio-geographical classification of India, Importance of Bio-Diversity Constructive and Destructive application, Importance of social, moral and alternative vision, Global, National and Local level Bio-diversity, India as a mega biodiversity nation, Hotspots of Biodiversity, threats to biodiversity, loss of habitat, damage to wildlife, humans and wild animals conflict, India's threatened.endangered and endamic species, Conservation of bio-diversity, Topological and Nontopological conservation. Enviromental pollution Causes, effect and control measures- Air pollution, water pollution, marine pollution, soil pollution, sound/noise pollution, thermal pollution, nuclear pollution. Solid waste managment Urban and Industrial solid waste management: Causes, effect and control, Human role in pollution control.
QUESTION PAPER-05
General Studies - III
PART-01 Economics of India & Chhattisgarh:-
1. National and per capita income, Structural changes in the Indian Economy (GDP and work force), Changes in the role of Public and Private Sectors and their shares in the total plan outlay of the latest plan, Economic Reforms, problems of poverty and unemployment, magnitude and measures initiative to ameliorate them, Monetary Policy- structure of Indian Banking and non-banking financial institutions and reforms in them since 1990s. Regulation of Credit by RBI. Pattern of Public Revenue, Public Expenditure, Public Debt, fiscal deficit and their effects on the Economy.
2. In Reference with C.G. - Demographic features and social backwardness of the Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Backward classes and Minorities. Literacy and occupational structure, changes in the sectoral distribution of income and employment. Socio, Political and Economic empowerment of Women. Child Labour problem. Rural Development, State Finance and Budgetary policy- Tax structure, Sharing in Central Taxes, Expenditure pattern in Revenue and Capital Account as well as plan and non-plan expenditure. Public Debt composition- Internal and External Debt including World Bank loans, Institutional and non-institutional sources of Rural Credit in Chhattisgarh. Structure and growth of Co-operatives and their shares in total credit, adequacy and problems.
PART-02 Geography of India:-
Physical features of India, location & extension, Geological Structure, Physical Divisions, Drainage System, Climate, soil, Vegetation and importance of forest, Indian forest policy. Forest conservation, Human Characteristics Population, Census, Population Growth, Density and Distribution. Birth rate, Mortality rate, Infant Mortality rate, Migration, Literacy, Occupational Structure, Urbanization, Agriculture Characteristics of Indian agriculture, Agricultural food Crops, Cereal, Pulses, Oilseeds and other crops, Production and distribution, mean of irrigation and its importance, Modernization of agriculture, problems of agriculture and planning, Irrigation multipurpose projects, Green revolution, white revolution, Blue revolution, Mineral resources- mineral storage, production and distribution of mineral, Energy resources coal, Petroleum, thermal power energy, nuclear energy, non conventional sources of energy. Industries- development and structure of industries in India, large Scale medium, small and smallest scale, agriculture, forest and mineral based industries.
PART-03 Geography of Chhattisgarh:-
Physical features of Chhattisgarh, location & extension, Geological Structure, Physical Divisions, Drainage System, Climate, soil, Vegetation and wild life, importance of forest, wild life management system, national parks and sanctuaries, State forest policy, Forest conservation, Human Characteristics Population, Population Growth, Density and Distribution. Birth rate, Mortality rate, Infant Mortality rate, Migration, Sex ratio, age group, schedule caste population Literacy, Occupational Structure, Urbanization, family welfare programs. Agriculture Agricultural food Crops, Cereal, Pulses, Oilseeds and other crops, Production and distribution, mean of irrigation and its importance, important irrigation projects, problem of agriculture and state scheme for farmers benefits, Mineral resources- various types mineral storage in Chhattisgarh, production and distribution of mineral, Energy resources- coal, Thermal power energy, non conventional sources of energy. Industries- development and structure of industries in Chhattisgarh, large Scale medium, small and smallest scale, agricultural, forest and mineral based industries, mean of transport and tourism.
QUESTION PAPER-06
General Studies - IV
PART-01 Philosophy:-
Nature of Philosophy, its relationship between religion and culture, difference between Indian and Western Philosophy, Veda and Upanishada-Brahman, Atman, Rit, Philosophy of Gita Sthitpragya, Swadharma, Karmayoga, Philosophy of Charvaka-Epistemology, Metaphysics, Hedonism, Philosophy of Jain Nature of Jiva, Anekantvada, Syadavada, Panchamahavrata, Philosophy of Buddha Pratityasamutpada. Ashtanga Marg, Anatmavada, Kshanikvada, Philosophy of Samkhya Satkaryavada, nature of Prakriti and Purusha, Vikasavada, Philosophy of Yoga Ashtanga Yoga, Philosophy of Nyaya
Prama, Aprama, Asatkaryavada, Philosophy of Vaisheshika Parmanuvada, Philosophy of Mimamsa Dharma, Theory of Apurva, Philosophy of Advaita Vedanta- Brahman, Maya, Jagat, Moksha, Kautilya Theory of Saptanga, theory of Mandal, Gurunanak Social-ethical philosophy, Guru Ghasidas Characteristics of Satnam Pantha, Vallabhacharya Pushtimarga. Swami Vivekananda Practical Vedanta, Universal Religion, Sri Aurbindo intergral yoga, supermind Mahatma Gandhi- Ahinsa, Satyagraha, elevan vows, Bhimrao Ambedkar Social Thought, Deendayal Upadhyay Ekatma manav darshan, Plato Virtus, Aristotle Theory of Causation, Saint Anselm Ontological argument for the existance of God, Descartes method of doubt, I think therefore I am, Spinoza Substance, Pantheism, Leibnitz theory of Monad, Theory of Pre stablished harmony. Locke epistemology, Berkeley - esse est percipii, Hume Scepticism, Kant - Criticism, Hegel - Phenomenology and spirit, dialectical Idealism, Bradley Idealism. Moore Realism, A.J. Ayar Verification theory, John dewey Pragmatism, Sartre Existentialism, Meaning of Religion, Nature of Philosophy of Religion, Religious tolerance, secularism, problem of evil, Ethical Values and ethical Dilemma, ethical elements in Administration- Honesty, Responsibility, Transparency, Code of conduct for Public Servants. Corruption - Meaning. Types, Cause and Effect, Efforts to remove corruption. Relevence of whistle-blower.
PART-02 Sociology:-
Sociology- Meaning, Scope and nature, Importance of its study. Relation with other Social Sciences. Primary Concepts Society, Community, Association, Institution, Social group, Folkways and Mores. Individual and Society Social interactions, Status and role, Culture and Personality. Sociolization. Hindu Social Organization Religion, Asharm, Varna, Purusharth. Social Stratification Caste and Class. Social Processes Social Interaction, Co-operation, Struggle, Competition. Social Control and Social Change Sources and agencies of Social Control, Processes and factors of Social Change. Indian Social Problems, Social disorganization-Anomie and Alienation, Inequality. Social Research and Techniques Objective of Social Research. Use of scientific method to study of Social Phenomena, Problems of objectivity. Tools and techniques of data collection- Observation, Interview, Questionnaire, Schedule.
PART-03
Social Aspect of Chhattisgarh:- Tribal social organization: Marriage, Family, Clan, youth dormitories. Tribal Development: History, Programmes and Policies, The Constitutional System, Special Primitive Tribes of Chhattisgarh, Other Tribes, Schedule Cast and Other Backword Class of Chhattisgarh. Main Ornaments popular in tribes of Chhattisgarh, Special traditions. Tribal Problems: Isolation Migration and acculturation. Folk arts of Chhattisgarh, Folk literature and Prominent Folk Artists of Chhattisgarh, Folk songs of Chhattisgarh, Folk legend, Folk theater, Idioms and Proverbs, Puzzle/riddle (जनऊला), Singing (हाना), Literary, Music and Art Institutions of Chhattisgarh State; Chhattisgarh State awards in these fields. Folk culture of Chhattisgarh, Major Fairs and Festivals of Chhattisgarh. Protected Archaeological monuments, sites and excavated sites in State. Tourism places marked by Chhattisgarh Govt., National Parks, Sanctuaries and Waterfalls and caves of Bastar, Major sants of Chhattisgarh.
QUESTION PAPER-07
General Studies - V
PART-01 Welfare, Development Programme & Laws:-
1. Social and Important Legislation Indian Society, Social legislation as a form of a mean of social transform. Human Rights Proctection Legislation 1993, Protection granted to Females (CRPC) under Indian Constitution & Criminal Law (Penal Code). Protection Act 2005 to Females from Domestic Violation, Civil Rights Protection Act 1955, Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes Attrocity Protection Law 1989, Right to Information Act 2005, Environment Protection Act 1986, Consumer Protection Act 1986, Information Technology Act 2000, Curruption Prevention Act 1988.
2. In Reference to Chhattigarh: Customary Various Laws and Acts in Chhattisgarh and their welfare and developmental impact on residents of Chhattisgarh.
3. Welfare Schemes of Chhattisgarh Government: Customary welfare, People-oriented and Important Schemes introduced in various times by Chhattisgarh Government.
PART-02 International & National Sports, Events & Organisation:-
United Nations and its Associated Organizations. International Monetary Fund, World Bank and Asian Bank, SAARC, BRICS, Other Bilateral and Regional Groups, World Trade Organization and its impact on India. National and International Sports and Competition.
PART-03 International & National Educational Institute & their Role of Human Development:-
Availability of Skilled Human Resources, Employability and Productivity of Human Resources. Various Trends of Employment. Role of Various Institutions and Councils in Human Resources Development as Higher Education and National Commission for Research, National Educational Research and Training Council, National Educational Schemes and Administration University, University Grants Commission, Open University, All India Technical Education Council, National Education Teacher Council, National Vocational Education Council, Indian Agriculture Research Council, Indian Institute of Technology, Indian Institute of Management, National Institute of Technology, National Law University, Polytechnique and I.T.I., Education in Human Resource Development, a mean Universal/Equal Elementary Education, Higher Education and Technical Education, Quality of Vocational Education, Issues related to Girls' Education, Deprived Class, Issues related to Disabled People.